Understanding the Current Trends in World Population
Introduction
The world population has long been a critical measure of human development, resource allocation, and environmental sustainability. As of October 2023, the global population is projected to surpass 8 billion individuals, highlighting the immense challenges and opportunities faced by governments, organisations, and communities worldwide. Monitoring population changes is vital for effective policy-making and planning for future needs, such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
Current Population Dynamics
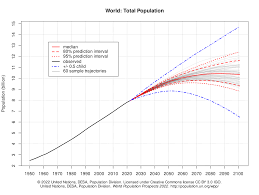
According to the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA), the world population reached 8 billion on November 15, 2022. The population growth rate is gradually slowing, with projections estimating a rise to approximately 9.7 billion by 2050. This growth is driven by several factors, including high birth rates in certain regions and increased life expectancy due to advancements in healthcare and nutrition.
Geographically, population growth is not uniform. Countries in sub-Saharan Africa are experiencing the fastest growth rates, while many nations in Europe and East Asia, such as Italy and Japan, are witnessing a decline in population due to low fertility rates and aging demographics. This discrepancy poses unique challenges, such as labour shortages in aging societies and overcrowding in regions with rapid growth.
Implications of Population Growth
The significance of the world population trend cannot be understated. Increased population density often leads to higher demands for resources including food, water, energy, and housing. Governments are urged to innovate and implement sustainable practices to manage these finite resources effectively. Furthermore, urbanisation is rising, with an expected 68% of the global population residing in cities by 2050. This migration necessitates infrastructure development and efficient public services to accommodate growing urban environments.
Moreover, the escalating population affects climate change, as larger populations tend to contribute to higher carbon footprints and environmental degradation. Addressing these concerns requires collaborative efforts from international organisations, policymakers, and local communities.
Conclusion
The world population is expected to reach 9 billion by 2050, necessitating urgent action and innovative solutions to tackle the profound challenges faced by society. Understanding population trends is essential for shaping effective strategies in governance, economic planning, and environmental stewardship. The sustainability of our planet and the quality of life for future generations largely depend on how we manage the impact and implications of population growth today. As we progress, continuous research and dialogue will be key to navigating this complex landscape.









