Understanding Chikungunya: Outbreaks, Symptoms, and Prevention

Introduction
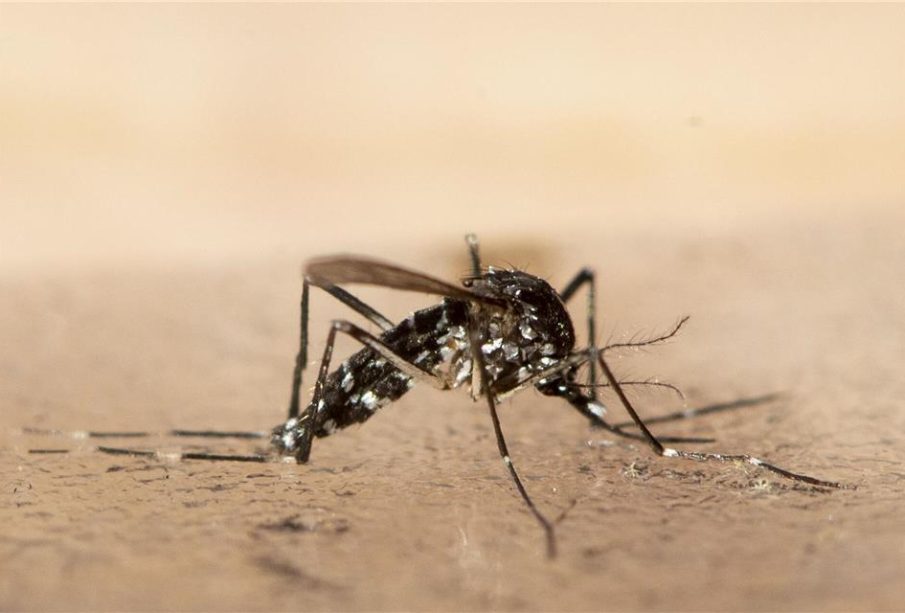
Chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted by mosquitos, primarily Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Its importance has surged due to recent outbreaks in various regions globally, raising concerns about public health. With symptoms that can lead to long-term joint pain and no specific antiviral treatment available, understanding this disease is crucial for both prevention and management.
Current Outbreaks and Statistics
Recent reports from the World Health Organization (WHO) indicate that chikungunya cases have seen a dramatic increase in 2023, especially in parts of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. For instance, countries like India and Brazil have reported thousands of confirmed cases, leading to increased healthcare scrutiny and preventive measures. In the first quarter of this year, Brazil registered over 15,000 cases, eclipsing previous yearly totals and indicating a worrying trend that could escalate if the vector control measures are not effectively implemented.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Chikungunya virus typically presents symptoms such as high fever, severe joint pain, muscle pain, headache, fatigue, and rash. Symptoms usually appear three to seven days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. While most patients recover within a week, some may experience arthritis-like symptoms for months or even years, making accurate diagnosis and appropriate management essential.
Preventive Measures
Preventing chikungunya primarily involves reducing mosquito bites and controlling breeding grounds. Experts recommend using mosquito repellent containing DEET, wearing protective clothing, and ensuring that homes and communities are free from standing water where mosquitoes breed. Public health campaigns are also critical, educating communities on how to protect themselves and reduce the risk of outbreaks.
Conclusion
As haya chikungunya continues to pose a threat in various regions, awareness and prevention are vital. The global community must focus on vector control and public health initiatives to mitigate the spread of this virus. With changing climate conditions potentially expanding the range of Aedes mosquitoes, ongoing monitoring and rapid response to cases will be imperative. Understanding and managing chikungunya today can save communities from larger outbreaks in the future.