The Impact of Ultra Processed Foods on Health
Introduction
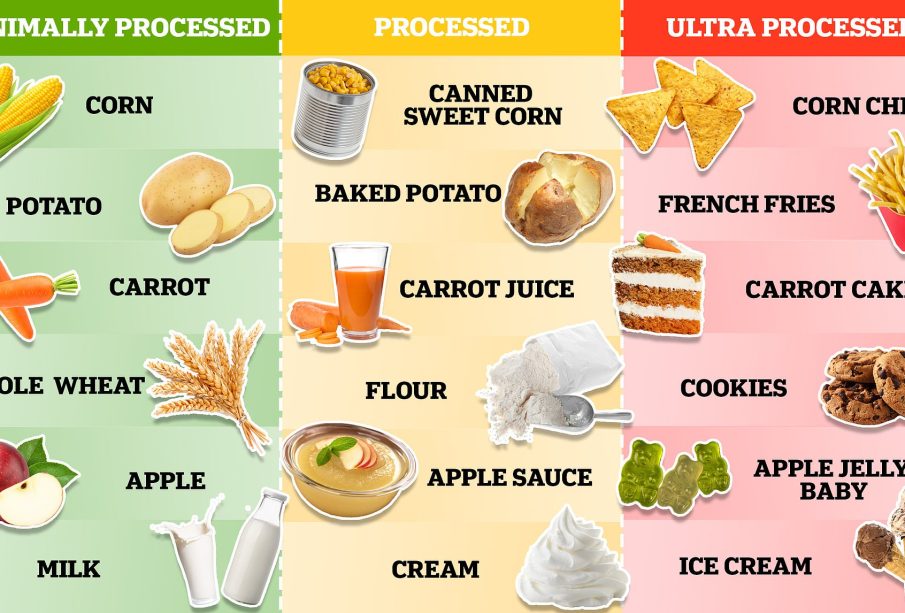
In recent years, the consumption of ultra processed foods has become a pressing topic in the fields of nutrition and public health. Defined as industrial formulations typically containing five or more and usually many more and ingredients, these products include additives like preservatives, sweeteners, and artificial flavourings. As modern lifestyles continue to grow busier, ultra processed foods increasingly dominate our diets, raising significant concerns regarding their health implications.
The Rise of Ultra Processed Foods
The prevalence of ultra processed foods has surged in the United Kingdom and across the globe, driven by convenience and aggressive marketing strategies. According to a report from the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), around 50% of all food purchased in the country is now classified as ultra processed. This shift has implications not only for individual health but also for the broader healthcare system, as rising consumption is intimately linked with increasing rates of obesity and related diseases.
Health Implications
Numerous studies have highlighted the detrimental effects of consuming ultra processed foods. Research published in the British Medical Journal indicates that increased intake of these foods correlates strongly with obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. The high levels of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats commonly found in these products can lead to poor dietary quality and elevate the risks of chronic health conditions.
Additionally, a review published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition emphasizes that these foods often displace nutrient-dense options, which are essential for maintaining overall health. As ultra processed foods tend to be low in fibre and various nutrients, their excessive consumption often leads to a deficiency in essential vitamins, and minerals.
Government and Public Responses
In light of these alarming trends, various governmental and health organisations have begun addressing the issue. Efforts include educational campaigns aimed at raising awareness about the importance of choosing whole and minimally processed foods over their heavily processed counterparts. The UK government has also introduced measures like the Soft Drink Industry Levy to reduce sugar intake from beverages, which often fall into the ultra processed category.
Conclusion
The implications of ultra processed foods on health cannot be overstated. As their presence continues to grow within our diets, individuals are urged to critically evaluate their eating habits. Furthermore, governments and communities must work collaboratively to promote healthier eating choices. Predictions suggest that without significant changes in consumer habits and food industry practices, the prevalence of diet-related health issues will rise, putting additional strain on public health resources. Thus, understanding the effects of ultra processed foods is crucial for fostering a healthier future.