What You Need to Know About Lyme Disease
Introduction to Lyme Disease
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness caused by the bacterium *Borrelia burgdorferi*. It has garnered increasing attention in recent years due to a rise in reported cases, particularly in Europe and North America. A rise in tick populations and changing climate conditions contribute to this increase, making awareness and education about the disease crucial for public health.
Recent Trends and Statistics
According to the latest reports from Public Health England, the incidence of Lyme disease in the UK has experienced a significant uptick, with approximately 2,000 confirmed cases each year. This increase correlates with warmer weather patterns, which have expanded the habitats suitable for ticks. In 2023, regions in the South of England, including Surrey and the New Forest, have reported the highest numbers of cases, underscoring the need for vigilance in these areas. Outdoor enthusiasts, particularly hikers and campers, are at a higher risk of exposure.
Recognising Symptoms
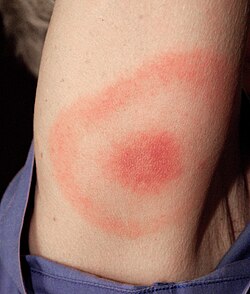
Early recognition of Lyme disease is vital for effective treatment. Initial symptoms may include fever, headache, fatigue, and a characteristic skin rash known as erythema migrans, which resembles a ‘bull’s-eye’. If left untreated, Lyme disease can lead to more severe health issues, such as joint pain, neurological problems, and cardiac complications. The diversity of symptoms can lead to misdiagnosis, making awareness essential for timely medical intervention.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventative measures play a crucial role in reducing Lyme disease transmission. Health officials recommend wearing long sleeves and trousers when in wooded or grassy areas, using tick repellents, and conducting thorough tick checks post outdoor activities. If Lyme disease is suspected, a healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics, which are typically effective when treatment is initiated early. Education and community awareness are pivotal in combatting the spread of this disease.
Conclusion: The Future of Lyme Disease Awareness
As climate change continues to reshape environments, the tick population is expected to grow, potentially increasing Lyme disease cases. Public health initiatives focus on education, prevention, and research into vaccines. For individuals, staying informed and taking precautions can significantly reduce the risk of Lyme disease. As we move forward, continuous collaboration between health authorities and communities will be vital to address this public health challenge effectively.