Understanding West Nile Virus: Current Trends and Insights
Introduction
The West Nile Virus (WNV) is a mosquito-borne pathogen that poses a significant threat to public health, particularly during warmer months. It was first identified in the United States in 1999, and since then, the frequency and severity of outbreaks have raised concerns among health officials. Understanding the current status of WNV is essential as we navigate the complex landscape of infectious diseases, especially with the ongoing effects of climate change that may influence mosquito populations.
Current Outbreak Trends
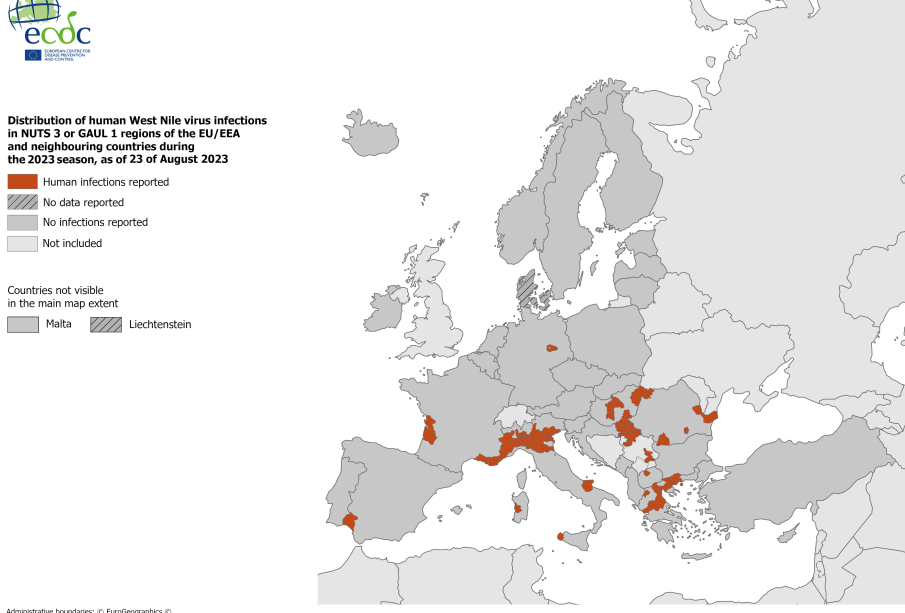
As of 2023, there have been several reported cases of West Nile Virus across the United States, with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) noting a notable rise in infections, particularly in the Midwest and Southern states. According to the latest statistics, over 150 cases of neuroinvasive disease caused by WNV have been documented this year, reflecting a worrying trend compared to previous years.
The increase in cases is attributed to several factors, including a particularly active mosquito season, environmental conditions favouring mosquito breeding, and factors related to human behaviour such as increased outdoor activities during the pandemic. Public health officials are concerned that these factors, combined with the expansion of WNV into new regions, could lead to further outbreaks, necessitating heightened awareness and preventive measures.
Preventive Measures and Public Health Responses
In response to the ongoing threat of West Nile Virus, various public health initiatives are being implemented across affected regions. These measures include increased mosquito surveillance and control efforts, public awareness campaigns to educate communities on preventing mosquito bites, and promoting the use of repellents and protective clothing.
Communities are also being encouraged to eliminate standing water where mosquitoes breed, reinforcing the importance of personal and communal responsibility in disease prevention. Health authorities are working in collaboration with environmental agencies to monitor mosquito populations and track any changes that could lead to increased transmission of WNV.
Conclusion
The rise of West Nile Virus cases this year illustrates the ongoing need for vigilance and proactive public health measures. As we continue to see fluctuations in disease patterns due to environmental changes, it is crucial for communities to remain informed and prepared. Future forecasts suggest that with proper preventive strategies, the impact of West Nile Virus can be mitigated, ensuring better protection for vulnerable populations. Ultimately, the path towards managing WNV outbreaks lies in comprehensive education, responsible behaviour, and community engagement in public health efforts.