Understanding the Importance of the HPV Vaccine
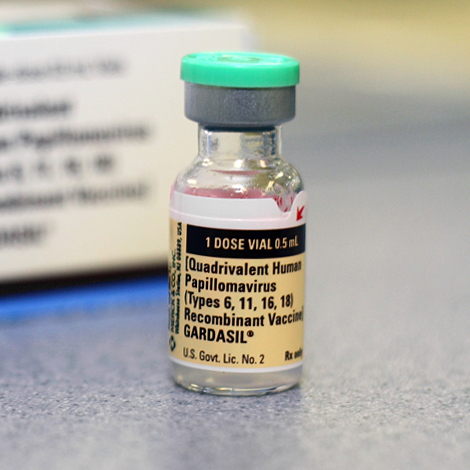
Introduction
The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine has become a crucial tool in preventing certain types of cancers, particularly cervical cancer. HPV is a widespread virus that can lead to various cancers, including those of the cervix, anus, throat, and penis. With vaccination programs ramping up globally, the importance of the HPV vaccine cannot be overstated, as it presents a significant opportunity to reduce cancer incidence and related healthcare burdens.
What is the HPV Vaccine?
The HPV vaccine protects against the types of HPV that most commonly cause these cancers. There are currently three vaccines available: Gardasil, Gardasil-9, and Cervarix, with Gardasil-9 being the most widely recommended as it protects against nine HPV types. Health authorities recommend vaccinating preteens aged 11 to 12 years, but it can be administered to individuals up to age 26. In some cases, vaccination can be considered for those up to age 45.
Current Developments and Coverage
Recent studies highlight an increase in the success rates of HPV vaccination programmes. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as of 2022, over 100 countries have introduced the HPV vaccine into their national immunisation schedules. This shift is particularly relevant as cervical cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer death among women worldwide. A report by Public Health England indicated that HPV vaccination has led to a remarkable 87% reduction in HPV infections among vaccinated girls, highlighting its efficacy and potential for long-term impacts.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the progress, challenges remain regarding the uptake of the vaccine. Misconceptions about the vaccine, access issues in some regions, and concerns about vaccine safety continue to deter individuals from getting vaccinated. To combat these challenges, campaigns focusing on education and raising awareness about the benefits and safety of the HPV vaccine are essential. Health authorities are actively working towards eliminating cervical cancer as a public health problem by emphasising the importance of vaccination, regular screening, and early detection.
Conclusion
The HPV vaccine represents a pivotal advancement in cancer prevention. By reducing the incidence of HPV-related cancers, especially cervical cancer, this vaccine holds the promise of saving lives and alleviating the burden on health systems. As education and awareness grow, coupled with improved access and availability of the vaccine, the global community is hopeful for a significant reduction in HPV-related cancer rates. The importance of the HPV vaccine must continue to be reinforced for future generations to ensure lasting health benefits.