Understanding the Gen Z Years: Characteristics and Impact
Introduction to Gen Z Years
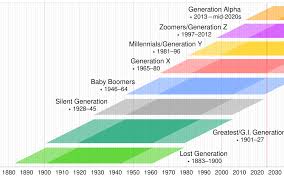
As the youngest generation in the workforce and society, Generation Z (Gen Z) has emerged as a significant force shaping culture, technology, and social dynamics. Born roughly between 1997 and 2012, Gen Z years represent a period of unprecedented change and adaptation, heavily influenced by the digital world and social media. Understanding this generation is crucial not only for businesses targeting them as consumers but also for society at large, given their unique perspectives and approaches to issues such as climate change, mental health, and social justice.
Defining Characteristics of Gen Z
One of the primary characteristics of Gen Z is their keen usage of technology. Growing up in a world dominated by smartphones and social media, they are often described as “digital natives”. This proficiency has led to a distinctive communication style, prioritizing quick exchanges through platforms like TikTok and Snapchat. According to a recent survey by Pew Research, over 95% of Gen Z members own a smartphone, highlighting their dependence on technology for communication and information.
Social consciousness is another defining trait of Gen Z. This generation is notably vocal about issues like climate change, social equity, and mental health. They utilize online platforms to advocate for change and engage in activism, often leading campaigns that challenge traditional narratives. The global climate strikes initiated by youths worldwide illustrate their commitment to environmental issues and their willingness to mobilize for causes they believe in.
Impacts on Society and the Workforce
The distinct characteristics of Gen Z are influencing both society and the workplace. In the workplace, companies are beginning to adopt more flexible working conditions and prioritize mental health initiatives to attract young talent. A report by Deloitte found that Gen Z values workplace diversity and expect employers to take meaningful actions towards inclusion. They also seek jobs that align with their personal values, challenging employers to rethink their corporate social responsibilities.
In the realm of popular culture, Gen Z is driving trends that prioritize inclusivity and authenticity. Their preference for brands that represent diverse identities has changed marketing strategies across various industries. Businesses are increasingly leveraging user-generated content and influencer collaborations to connect with this demographic.
Conclusion
The years of Gen Z offer valuable insights into the future direction of societal norms and consumer behaviour. As this generation continues to mature and enter adulthood, their influence will expand, shaping political, environmental, and social landscapes. For businesses, understanding the nuances of Gen Z years is pivotal in navigating the new paradigms of consumer engagement and workplace dynamics. As we move forward, keeping a close eye on this generation’s evolution will be essential for anticipating shifts in culture and the market.









