Understanding the Bubonic Plague in the Modern World
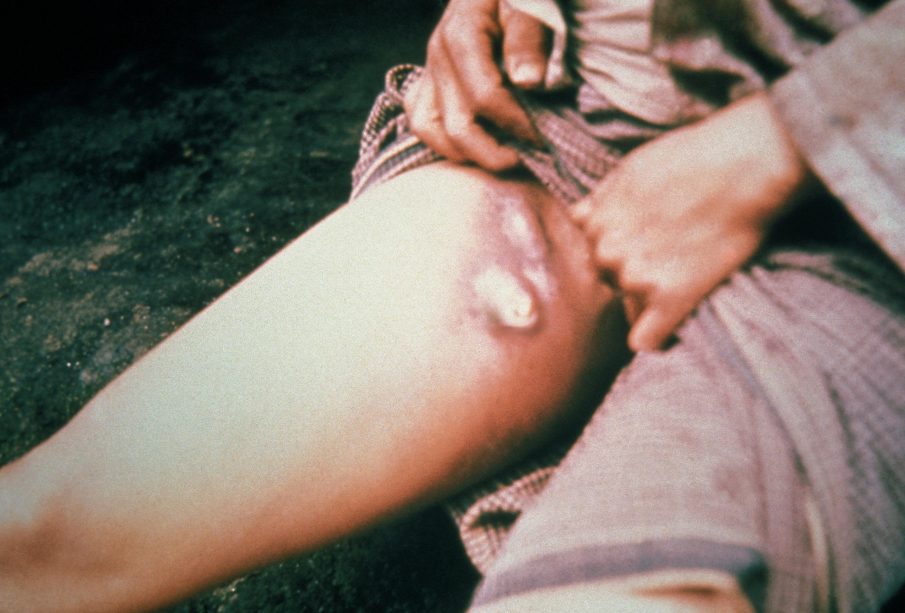
Introduction to the Bubonic Plague
The bubonic plague, historically infamous for causing the Black Death in the 14th century, remains a topic of concern due to its sporadic occurrences in modern times. Although overshadowed by more contemporary diseases, understanding the bubonic plague’s current status and its implications for public health is crucial. With an increase in cases reported globally, it is vital to assess its significance and the measures in place to control potential outbreaks.
Current Events and Statistics
As of 2023, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has reported a small number of bubonic plague cases in the United States, mainly concentrated in the southwestern region. In 2022, the state of New Mexico recorded five cases, a slight increase from the preceding year, which underscores the ongoing nature of this disease. Globally, countries such as Madagascar and the Democratic Republic of Congo continue to report periodic outbreaks, with health organizations working to combat and monitor these incidents aggressively.
Transmission and Prevention
The bubonic plague is primarily transmitted through bites from infected fleas found on rodents. Understanding this mode of transmission is essential for implementing effective public health strategies. Awareness campaigns have been crucial in educating communities about preventing contact with potentially infected wildlife, maintaining proper sanitation, and monitoring for plague outbreaks. Efforts from the World Health Organization (WHO) and various health ministries have been vital in fostering a proactive approach to managing this age-old disease.
Conclusion and Significance
The bubonic plague, while not a widespread threat today, serves as a reminder of the persistent risks posed by infectious diseases. With climate change affecting rodent populations and altering ecosystems, the potential for increased transmission is a reality that many regions must consider. Experts predict that continuous monitoring, rapid response to isolated outbreaks, and public education are crucial to minimising risks associated with the bubonic plague. By remaining vigilant and implementing preventive measures, we can ensure that history does not repeat itself, and the lessons learned from the past continue to shape our responses to infectious diseases.