Understanding Marburg Disease: Risks and Responses
Introduction to Marburg Disease
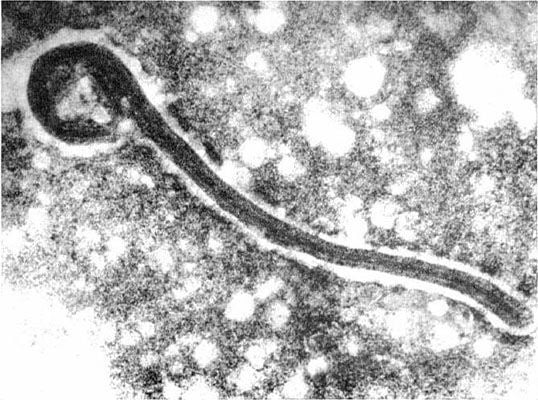
Marburg disease, caused by the Marburg virus, is a severe and often fatal disease that has emerged as a public health concern in recent years. Its high mortality rate, which can exceed 80% in some outbreaks, makes the understanding and prevention of this disease imperative. With an increase in reported cases, particularly in Africa, public health officials are on high alert. Understanding the nature of Marburg disease, transmission methods, and effective responses is crucial for safeguarding communities.
Recent Outbreaks and Public Health Response
In 2023, several cases of Marburg disease were reported in Equatorial Guinea, leading to heightened vigilance across the region. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared an outbreak when two deaths occurred in the Kie Ntem province in January. Amidst fears of cross-border transmission, rapid response teams have been deployed, focusing on contact tracing, which is vital to controlling any potential spread of the virus.
The response has included vaccination campaigns targeting healthcare workers and increased surveillance in neighbouring countries. Furthermore, authorities have worked to raise public awareness about the disease, including its symptoms, which can initially resemble other viral infections, making swift recognition challenging.
Understanding Symptoms and Transmission
Marburg virus is primarily transmitted to humans through the handling of fruit bats, which are considered the natural hosts of the virus. Human-to-human transmission can also occur through direct contact with bodily fluids of infected individuals, making it crucial for affected communities to practise strict hygiene measures.
Symptoms typically begin abruptly and can include fever, severe headache, muscle pains, and abdominal discomfort. As the disease progresses, individuals may develop severe bleeding, organ failure, and shock, worsening their prognosis. Prompt medical intervention is critical, but as of now, there are no proven vaccines or antiviral treatments specific to Marburg disease.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The resurgence of Marburg disease highlights the need for ongoing vigilance and preparedness, particularly in regions where outbreaks have been reported. Global health agencies are working collaboratively with local governments to enhance response strategies through improved surveillance systems and public education. Developing effective vaccines and treatments remains a priority for researchers.
Looking ahead, international cooperation and rapid health system responses will be essential to prevent the spread of Marburg disease. By raising awareness and investing in healthcare infrastructures, communities can better protect themselves against this formidable viral threat.