Understanding Lobular Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
Introduction to Lobular Cancer
Lobular cancer is an important subtype of breast cancer that originates in the lobules, the glands responsible for producing milk. It accounts for approximately 10-15% of all breast cancer diagnoses and is particularly relevant as awareness and early detection can significantly impact treatment outcomes. As health professionals and patients continue to adapt to advancements in medical research, understanding lobular cancer becomes increasingly critical.
What is Lobular Cancer?
Lobular cancer is characterised by the abnormal growth of cells within the lobules of the breast. Unlike the more common ductal carcinoma, which starts in the ducts that carry milk, lobular cancer often grows in a more subtle pattern, making it sometimes more challenging to detect through traditional screening methods like mammograms. It often presents as a thickening of breast tissue rather than a distinct lump.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
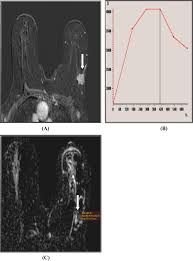
Common symptoms of lobular cancer include changes in the size or shape of the breast, the presence of a lump, or unusual swelling. However, because of its insidious nature, lobular cancer may not always show immediate symptoms. Regular screening and self-examinations are crucial for early detection. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of imaging techniques, such as mammograms and ultrasounds, alongside a biopsy to assess the nature of the tissue.
Treatment Options
Treatment for lobular cancer generally mirrors the approach for other types of breast cancer and may involve surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or hormonal therapy, depending on the cancer’s stage and characteristics. Stage I and II diseases can often be treated successfully with surgery and followed up with adjuvant therapies to help prevent recurrence. In cases of hormone receptor-positive lobular cancer, hormonal therapies like tamoxifen or aromatase inhibitors may also be effective. Moreover, clinical trials are actively researching targeted therapies that could improve outcomes for lobular cancer patients.
Conclusion
Understanding lobular cancer is vital for timely diagnosis and effective treatment. As research advances, new therapies and screening methods offer hope for improved outcomes. Patients and healthcare providers must remain vigilant about the symptoms and seek regular check-ups to facilitate early detection. Increased awareness and research support may lead to breakthroughs that positively affect prognosis and quality of life for those at risk of or diagnosed with lobular cancer.