Understanding Legionnaires’ Disease: Outbreaks and Prevention
Introduction to Legionnaires’ Disease
Legionnaires’ disease is a severe form of pneumonia caused by the Legionella bacteria, often found in water sources like cooling towers and hot tubs. With recent outbreaks reported in various regions, understanding the disease’s transmission, symptoms, and preventive strategies has become more critical than ever, particularly for vulnerable populations.
Recent Outbreaks
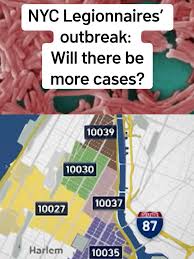
In August 2023, health officials in the United Kingdom reported a significant outbreak connected to a hotel in central London, where multiple cases were traced to contaminated water systems. Over 20 individuals have been diagnosed, prompting an urgent public health response. Investigators are now conducting thorough inspections of the hotel’s plumbing and water supply systems, with laboratory tests confirming the presence of Legionella bacteria.
Similarly, a report from Australia highlighted an increase in cases linked to a cooling tower at a large office complex in Melbourne. Authorities are emphasising the need for routine maintenance and monitoring of such facilities to prevent further cases.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Victims of Legionnaires’ disease often experience symptoms similar to those of influenza, including fever, chills, cough, and shortness of breath. Severe cases can lead to complications such as respiratory failure or septic shock. Diagnosis typically involves chest X-rays and laboratory tests to identify the bacteria in the patient’s lungs or urine.
Prevention and Control Measures
Preventing outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease primarily hinges on effective water management strategies in buildings. Routine inspection and maintenance of water systems are paramount. Facilities should ensure that cooling towers are regularly cleaned and disinfected. Additionally, maintaining water temperatures above 60°C (140°F) can significantly inhibit bacterial growth.
Conclusion and Future Implications
As outbreaks of Legionnaires’ disease continue to pose a public health challenge, awareness and proactive measures are vital. The recent instances in the UK and Australia underline the importance of stringent water management protocols in preventing disease transmission. Moving forward, increased vigilance in monitoring water systems across various facilities will be crucial in safeguarding public health and preventing future outbreaks. Staying informed about the risks and implementing preventive measures can help mitigate the impact of this potentially deadly disease.