Understanding ADHD Symptoms: Key Indicators and Insights
Introduction
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals across age groups. Understanding ADHD symptoms is crucial as early identification and intervention can significantly improve the quality of life for those affected. With recent studies highlighting an increase in diagnoses, this topic is particularly relevant today, enabling parents, educators, and individuals to recognise and address the symptoms effectively.
Main Symptoms of ADHD
ADHD symptoms can generally be categorised into two primary types: inattention and hyperactivity-impulsivity. Each individual may display symptoms differently, and these can evolve over time.
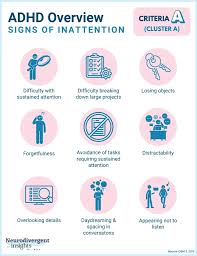
Inattention Symptoms: Individuals with ADHD may struggle to maintain focus, frequently missing details or making careless mistakes in schoolwork or other activities. Other signs include difficulty organising tasks, following through on instructions, and being easily distracted by extraneous stimuli. Those affected may also find it hard to listen when spoken to directly, often appearing to forget daily activities.
Hyperactivity-Impulsivity Symptoms: This component of ADHD manifests in behaviours such as fidgeting, excessive talking, difficulty sitting still, interrupting others, and acting without considering the consequences. These behaviours can lead to challenges in social and academic settings, as they often misinterpret social cues or disrupt others.
Diagnosis and Factors to Consider
Diagnosing ADHD typically involves a comprehensive evaluation, including behavioural assessments and input from parents, teachers, and medical professionals. It’s important to note that ADHD symptoms may resemble those of other conditions, such as anxiety or learning disabilities. Thus, a thorough examination is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Moreover, ADHD is influenced by various biological and environmental factors. Genetics play a significant role, but environmental components, such as prenatal exposure to tobacco or alcohol, can also contribute. Early research suggests that lifestyle factors, including diet and exercise, might influence the severity of symptoms.
Conclusion
Recognising ADHD symptoms is vital for individuals, families, and educators alike. Accurate identification leads to appropriate interventions, allowing those with ADHD to thrive. As awareness grows, ongoing research aims to improve our understanding of the condition, highlighting the importance of support systems and effective treatment options. By sharing knowledge about ADHD symptoms, we empower those affected and promote a more inclusive society where every individual can succeed.