Typhoid Fever: Current Trends and Health Implications
Introduction
Typhoid fever, caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi, is a life-threatening infectious disease that significantly impacts global health. Despite being largely preventable through vaccination and improved sanitation, it still poses a serious threat in many developing countries, particularly in regions with poor water quality and sanitation. With recent upticks in reported cases in various parts of the world, understanding typhoid fever’s implications remains crucial for public health.
Current Trends and Statistics
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 11 to 20 million cases of typhoid fever are reported annually, leading to around 128,000 to 161,000 typhoid-related deaths globally. Recent trends indicate a resurgence of cases, particularly in South Asia, where monsoon flooding and inadequate sanitation facilitate the spread of the disease. In 2023, countries like Bangladesh and India have witnessed a notable increase in typhoid fever cases linked to environmental factors and population density.
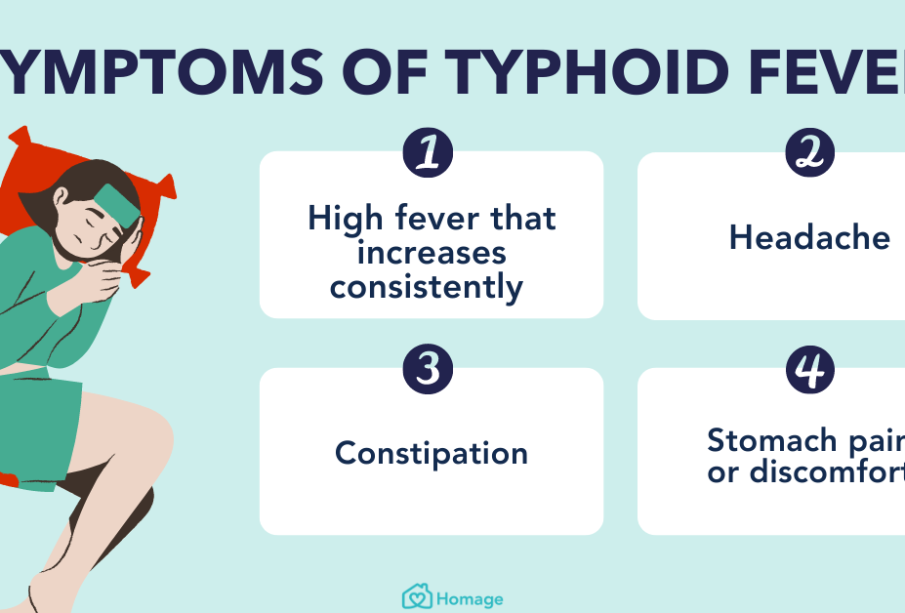
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Typhoid fever presents various symptoms including high fever, fatigue, headache, abdominal pain, and diarrhea or constipation. As the condition progresses, complications can occur if left untreated. Diagnosis typically involves blood cultures and specific serological tests to identify the presence of Salmonella typhi.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing typhoid fever is primarily focused on improving sanitation, providing access to safe drinking water, and vaccination. The WHO recommends typhoid vaccines for individuals in high-risk areas, providing a protective measure against this disease. Treatment involves the use of antibiotics; however, antibiotic resistance is an emerging challenge, making it vital to conduct proper susceptibility testing when managing cases. Public health education campaigns are also crucial to raise awareness about preventive measures, especially in endemic regions.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing typhoid fever is essential to reduce its prevalence and impact on communities worldwide. With recent fluctuations in incidence rates, public health initiatives must prioritize vaccination programs, promote sanitary practices, and enhance healthcare infrastructure. The fight against typhoid fever is ongoing, and collaboration between governments, healthcare professionals, and communities is paramount to effectively combatting this public health threat.








