The Rise and Impact of Ultra Processed Foods
Introduction to Ultra Processed Foods
In recent years, ultra processed foods have become a significant topic of conversation among health professionals, nutritionists, and the general public. These foods, often high in sugars, unhealthy fats, and artificial additives, are prevalent in modern diets, raising concerns about their impact on health. As lifestyles become busier and convenience becomes paramount, understanding the implications of consuming these foods is more crucial than ever.
What Are Ultra Processed Foods?
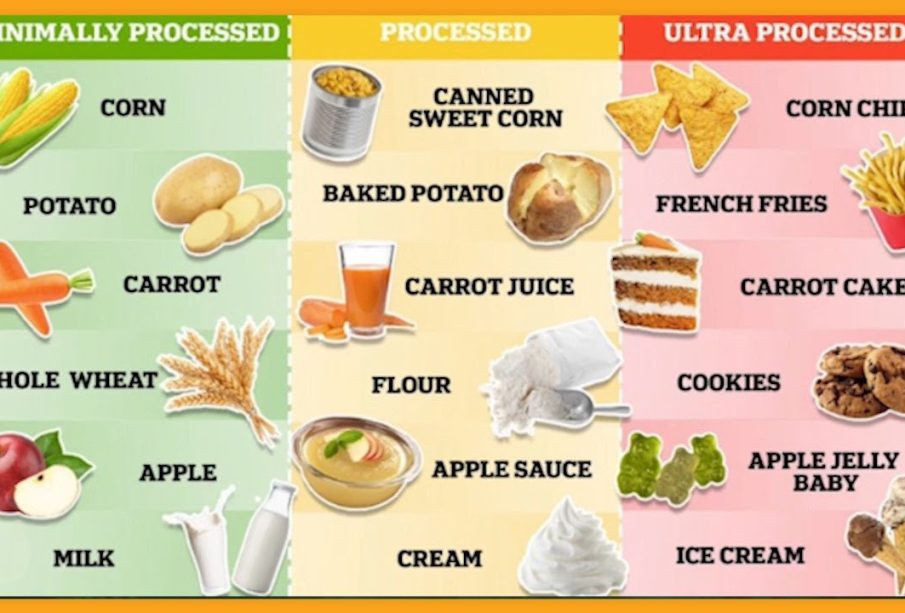
Ultra processed foods are defined as products that are manufactured using industrial processes and contain ingredients not typically found in a home kitchen. Common examples include sugary drinks, packaged snacks, instant noodles, and ready-to-eat meals. According to research from the World Health Organization, the consumption of such foods is linked to various health issues, including obesity, heart disease, and diabetes.
The Current Landscape
Recent studies highlight a worrying trend: ultra processed foods now account for around 50-60% of total calorie intake in several countries, including the UK. Data from the National Diet and Nutrition Survey indicates that intake has steadily increased over the past two decades. This trend correlates with rising rates of obesity and diet-related diseases, prompting health officials to call for a reevaluation of dietary guidelines.
Impact on Health
The negative health impacts associated with ultra processed foods are well-documented. A systematic review published in BMJ found a strong link between the consumption of these foods and increased risk of chronic diseases. The high sugar and fat content in these products can lead to metabolic issues, while additives and preservatives can have various adverse effects on health and wellbeing.
Public Response and Future Directions
In response to growing concerns, public health initiatives are being introduced globally to encourage healthier eating habits. Campaigns promoting whole foods, increased availability of fresh produce, and education on nutrition are gaining traction. The UK government is also considering policies aimed at reducing the marketing of ultra processed foods, particularly to children.
Conclusion
The discussion around ultra processed foods is more relevant than ever in today’s fast-paced society. As we become increasingly aware of the potential health risks associated with these products, there is a renewed emphasis on promoting better dietary choices. Consumers are urged to educate themselves about food labels and make informed decisions about their diet. The future of public health may depend on how effectively we can reduce the reliance on ultra processed foods and foster a culture of healthy eating.