The Polypill: A Breakthrough in Cardiovascular Health Management
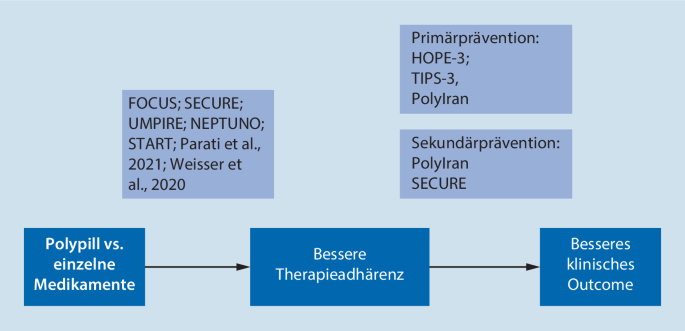
Introduction to the Polypill
The polypill has emerged as a significant innovation in the medical community, especially for those at risk of cardiovascular diseases. This combination pill, which typically includes aspirin, statins, and antihypertensive agents, aims not only to simplify medication regimens but also to enhance adherence and ultimately reduce the risk of heart-related events. As cardiovascular diseases remain a leading cause of mortality worldwide, understanding the implications of the polypill is essential for health professionals and patients alike.
Recent Developments
Recent studies have underscored the effectiveness of the polypill in various populations. A significant clinical trial published in the British Medical Journal in September 2023 found that patients taking a polypill had a 25% lower risk of heart attacks and strokes compared to those on traditional standalone medications. These findings are particularly promising for individuals over 50, as they represent the demographic most likely to benefit from multi-drug therapy. The simplicity of the polypill can lead to improved compliance, as fewer medications translate to less confusion for patients.
Global Impact and Accessibility
Countries like India and Chile have started to implement the polypill as part of their public health initiatives to combat cardiovascular diseases. In low-to-middle-income countries, where medication adherence can be significantly lower, the polypill may provide a cost-effective solution to reducing the healthcare burden of heart disease. However, challenges remain, such as ensuring the polypill is adequately accessible to all populations, along with awareness and understanding among both healthcare providers and patients.
Conclusion
The polypill represents a transformative step in the management of cardiovascular health. As more research supports its efficacy, it may soon become a standard part of treatment for those at risk. The potential benefits of reduced pill burden and increased adherence suggest that the polypill could significantly alter the landscape of cardiovascular disease management globally. As healthcare systems adapt to this new paradigm, ongoing monitoring of patient outcomes will be crucial for maximising the polypill’s impact on public health.