The Importance of State Pension in the United Kingdom
Introduction
The state pension is a crucial component of the UK’s social security system, providing financial support to millions of older adults. With the increasing ageing population and ongoing economic changes, understanding the state pension’s role has become more relevant than ever. As the UK faces challenges surrounding retirement funding, both current and future pensioners are keenly interested in the specifics of the state pension, its eligibility, and the reforms impacting it.
Current State Pension Structure
As of 2023, the UK operates two types of state pension: the basic state pension and the new state pension. The basic state pension is available for individuals who reached retirement age before 6 April 2016, while the new state pension applies to those who reached retirement age on or after that date. Currently, the full basic state pension is £141.85 per week, while the new state pension is £203.85 per week. These figures are subject to periodic increases, which are usually announced each April.
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for the state pension, individuals must have made a minimum number of National Insurance contributions throughout their working life. Typically, 10 qualifying years are necessary to gain any entitlement, with 35 years required for the full rate under the new state pension regime. However, changes to the state pension age, which currently stands at 66 for both men and women, may affect eligibility and retirement planning for many in the workforce.
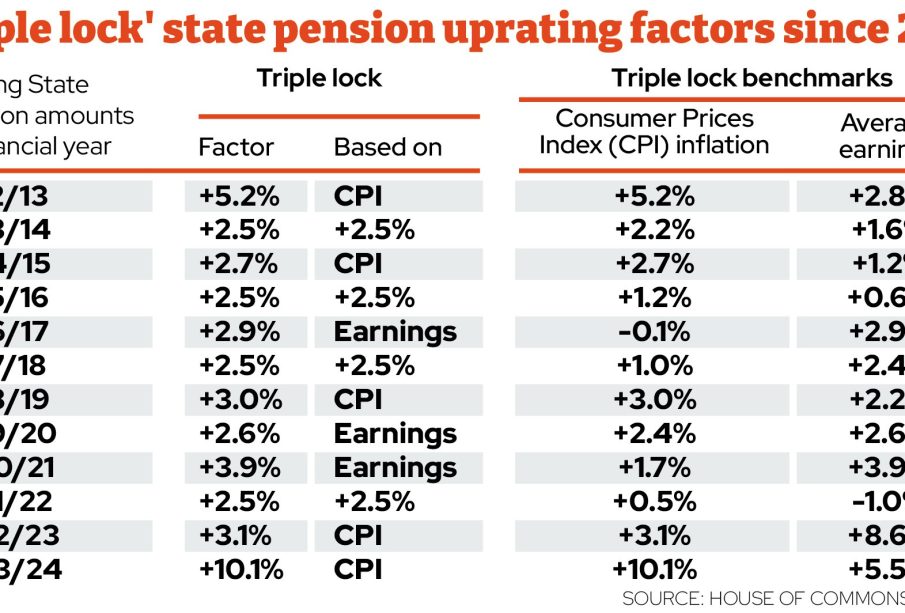
Recent Reforms and Future Impacts
The state pension system has undergone several reforms in recent years, aimed at making it sustainable in the long term. Notably, the triple lock guarantee, ensuring pensions increase by the highest of earnings, inflation, or 2.5%, has been a topic of debate. In 2022, the government temporarily suspended this policy amid economic pressures, causing concern among pensioners about future payments. Additionally, there are ongoing discussions about further adjustments to the state pension age, with potential increases beyond the current 66 years.
Conclusion
The state pension remains a vital financial resource for a significant portion of the UK’s population. As reforms continue to shape how pensions are distributed, it’s essential for individuals to remain informed about their entitlements. Given the uncertainty around pension ages and the sustainability of the funding model, individuals should consider their savings and investment strategies in conjunction with their state pension planning. Understanding these changes will Help citizens ensure financial stability in retirement, making it imperative to stay updated on any government announcements regarding the state pension.








