The Current State of Inflation: Trends and Implications

Introduction
Inflation, the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, is a critical indicator of economic health. In recent months, inflation has become a prominent topic globally, impacting consumers, businesses, and policymakers alike. Understanding inflation’s intricacies and its repercussions is essential, particularly in light of ongoing economic adjustments following the pandemic and geopolitical tensions.
Current Trends in Inflation
As of October 2023, the inflation rate in the UK stands at approximately 6.4%, a decrease from earlier highs of over 9% in 2022. This decline is attributable to several factors, including easing supply chain disruptions, lower energy prices, and decisive monetary policies implemented by the Bank of England. However, inflation remains above the target rate of 2%, indicating that the economy is still facing upward price pressures.
Food and energy prices have shown the most significant fluctuations. For instance, the price of basic food items increased by around 10% over the past year, driven by global supply chain constraints and increased production costs. Energy costs, which spiked dramatically in 2022, have since stabilised but remain a concern as geopolitical tensions continue to affect oil and gas markets.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
Inflation impacts consumers significantly, reducing purchasing power as the cost of living rises. Households are feeling the crunch, with many shifting spending habits to prioritise essential goods over discretionary purchases. Reports indicate that consumer confidence has dipped, with sentiments reflected in decreased sales figures in sectors like retail.
>Furthermore, businesses are grappling with increased costs, leading many to pass these expenses onto consumers in the form of higher prices. Small to medium enterprises (SMEs) are particularly vulnerable, as they have less pricing power compared to larger corporations. This dynamic can create challenges in maintaining customer loyalty and market share.
Policy Responses and Future Outlook
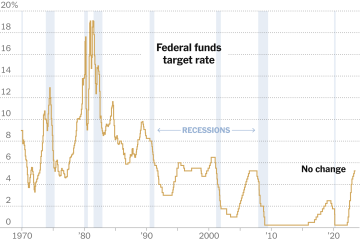
The Bank of England has responded to persistent inflationary pressures by increasing interest rates, aiming to cool down a rapidly growing economy. The latest hike brought the benchmark rate to 5.5%, the highest level since 2008. While this move seeks to moderate inflation, it also raises questions about the potential slowdown of economic growth and the implications for employment.
Looking ahead, economists predict that inflation will continue to pose challenges in the near term. Factors such as ongoing geopolitical tensions, labour market dynamics, and the global recovery from COVID-19 will play crucial roles in determining future inflation trajectories. For consumers and businesses alike, staying informed about inflation trends and adjusting strategies accordingly will be essential to navigating this complex economic landscape.
Conclusion
In summary, inflation remains a key topic with far-reaching implications for the economy and individual households. As trends evolve and policy responses adapt, it is vital for stakeholders to monitor developments closely. Understanding the factors behind inflation and its impacts can empower consumers and businesses to make informed decisions in an ever-changing economic environment.