The Current Landscape of AIDS: Trends and Treatment Options
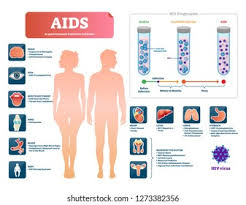
Introduction
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) continues to be a pressing global health issue more than 40 years after it was first identified. With millions of people living with HIV worldwide, advancements in treatment and prevention are critical for reducing transmission rates and improving the quality of life for those affected. Understanding the current trends in AIDS can help inform choices for individuals, health professionals, and policymakers alike.
Recent Developments in AIDS Research
In 2023, global health authorities report significant progress in AIDS treatment. Antiretroviral therapy (ART) remains the cornerstone of treatment. New research has revealed that early initiation of ART can lower the viral load in individuals living with HIV, resulting in better health outcomes and reduced transmission risks. Moreover, long-acting injectable treatments are gaining traction, offering patients a more convenient alternative to daily pill regimens.
Moreover, a recent study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association noted a promising correlation between preventative measures such as pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) and a decline in new HIV infections. This highlights the importance of continued education and access to prevention tools, particularly in high-risk communities.
Global Trends and Challenges
Despite the advancements, challenges remain. The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that nearly 38 million people are currently living with HIV, with a significant number still unaware of their status. Stigma and discrimination continue to hinder progress in treatment and prevention efforts, particularly in regions where poverty and lack of education exacerbate the situation.
Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted healthcare services globally, leading to decreased access to HIV testing and treatment in many countries. Health experts warn that this could result in a resurgence of new infections if not addressed comprehensively.
Conclusion
The landscape of AIDS treatment and prevention is continuously evolving, revealing both progress and persistent hurdles. As we advance, it is essential for individuals, health professionals, and government entities to work together to improve access to comprehensive healthcare services and education. Looking ahead, efforts focused on early diagnosis, stigma reduction, and sustained funding for AIDS programs will be crucial in the fight against this epidemic. By fostering awareness and empowering communities, we can aim to bring an end to AIDS by ensuring that every affected person has the ability to live a healthy, full life.





