Poland’s Bold Vision: Economic Growth and Political Reform Shape Nation’s Future in 2025
A Year of Transformation
Poland has embarked on a breakthrough year in 2025, as announced by Prime Minister Donald Tusk during a landmark speech at the Warsaw Stock Exchange, where he presented the country’s economic development strategy alongside Finance Minister Andrzej Domański.
Economic Developments and Growth
The government has launched an ambitious plan built on six key pillars: scientific advancement, energy transformation, modern technologies, port and railway development, capital market dynamism, and business support. This comprehensive strategy represents the largest investment package in Polish history, with a projected value of PLN 700 billion.
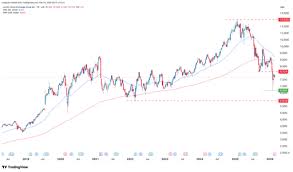
The economy has shown remarkable resilience, with GDP growth picking up to 2.9% in 2024. Private consumption has been the main growth driver, supported by increases in both nominal and real income. Looking ahead, while private consumption is expected to remain strong in 2025, investments are projected to drive growth, particularly in the public sector through EU-funded projects.
Technological and Infrastructure Advancement
Poland has established itself as one of Europe’s largest IT talent pools, boasting 400,000 specialists. This has attracted international companies to establish R&D centers in the country. The government has committed PLN 140 million for developing the fastest AI supercomputer, to be created by Polish IT experts and engineers.
Political Landscape and Reforms
Following the transition to a coalition government led by Donald Tusk in December 2023, Poland has been addressing rule of law concerns through various reform initiatives, including proposals for judiciary reform and steps to restore media freedom, though some measures have proven controversial. Progress on women’s and LGBT rights reforms has been gradual.
International Relations and Challenges
Poland faces several critical transitions requiring simultaneous attention: shifting towards a green economy, adopting digital technologies, and adapting to an aging population. These changes demand strong political leadership, institutional coordination, and administrative capacity at both national and subnational levels.
The country continues to play a significant humanitarian role, hosting over 970,120 Ukrainian refugees who have registered for temporary protection. However, challenges persist at the Belarus border, where migration management remains a complex issue.