Nissan’s Oppama Plant Closure: Impact and Implications

Introduction
The recent announcement of the closure of Nissan’s Oppama plant in Japan has sent ripples through the automotive industry and local communities. As production facilities adapt to shifting market demands, the closure raises questions about employment and Nissan’s long-term strategic direction. With the automotive landscape evolving, understanding the implications of this closure is crucial not only for stakeholders in Japan but also for global markets.
Details of the Closure
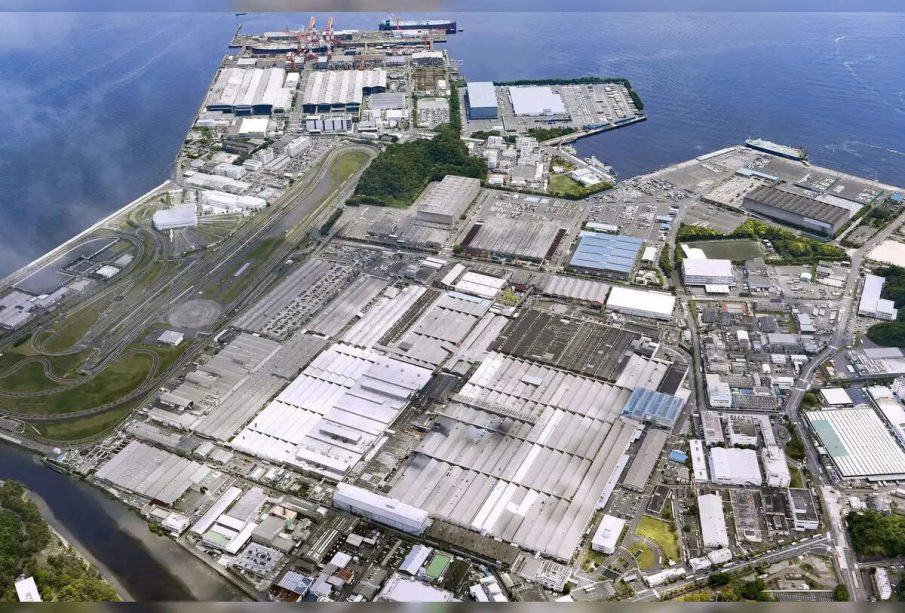
Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. confirmed that it will fully cease operations at the Oppama facility, which has been instrumental in producing various models since its inception in 1966. The decision, attributed to decreasing demand for certain vehicles and a strategic pivot towards electric and sustainable automobiles, reflects broader trends in the automotive sector. The plant employed over 3,000 workers and was known for manufacturing multiple models, including the popular Nissan Leaf and Serena.
The closure is expected to begin in early 2024, with operations gradually winding down in the months preceding. Nissan’s management indicated that the decision was made after considering various alternatives and the necessity to streamline production as they transition to a more future-oriented business model focusing on electric vehicles (EVs).
Impact on Local Economy
The closure of the Oppama plant is projected to have significant implications for the local economy. The facility supported thousands of jobs, and its shutdown is likely to create a ripple effect in the surrounding community. Local businesses, which relied on the custom of plant employees, are also anticipated to suffer. The municipality has expressed concern regarding the rising unemployment rates and is exploring potential measures to support affected workers through retraining programs and job placements.
Conclusion
Nissan’s decision to close the Oppama plant highlights the ongoing transformation within the automotive industry, particularly as manufacturers pivot towards electrification and sustainability. While the immediate impacts on employment and the local economy are concerning, the closure may also signify a larger trend towards innovation and advancement in automotive technology. As Nissan and other manufacturers adapt to changing consumer preferences, stakeholders will need to monitor the developments closely. The future of operations in Japan hangs in a delicate balance, and it remains to be seen how these changes will influence global automotive supply chains in the coming years.