Latest Developments on Marburg Virus Outbreaks
Introduction to Marburg Virus
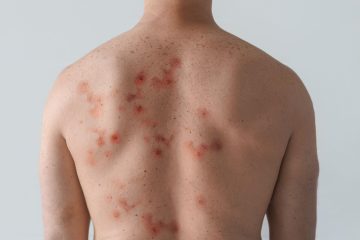
The Marburg virus, a highly infectious pathogen belonging to the filovirus family, can lead to severe viral hemorrhagic fever in humans. First discovered in the late 1960s during outbreaks in Marburg and Frankfurt, Germany, this virus has gained renewed attention following its recent outbreaks in Africa. The significance of understanding Marburg lies not only in its lethality but also in its potential to trigger public health emergencies, impacting regions where it spreads.
Current Outbreaks and Response Efforts
As of late 2023, the World Health Organization (WHO) is closely monitoring an outbreak of the Marburg virus in Ghana, where cases have risen since the first reports in early July. The Ghanaian government, alongside international health bodies, has initiated rapid response measures. These include setting up treatment centres, deploying healthcare workers, and instigating awareness campaigns aimed at educating the public about symptoms and transmission.
Global Health Systems at Risk
This outbreak underscores the need for strengthened healthcare systems, particularly in regions susceptible to outbreaks of infectious diseases. The Marburg virus, with a mortality rate that can exceed 90%, poses an extreme threat to global health security. The WHO has emphasised the importance of surveillance and quick response capabilities to contain the spread and prevent localised outbreaks from becoming global health crises.
Preventive Measures and Future Outlook
Preventive measures against the Marburg virus primarily focus on public education to reduce transmission. This includes avoiding contact with infected individuals and wildlife, especially fruit bats, which are considered natural reservoirs for the virus. Vaccination research is ongoing, and trials for a potential vaccine have shown promising results.
Conclusion
The Marburg virus remains a critical public health concern, particularly given its high fatality rate and potential for outbreak scenarios. As health organisations work diligently to control the current outbreak in Ghana, there is a pressing need for global cooperation in research, vaccination, and awareness campaigns. The future management of the Marburg virus will depend on improved surveillance technologies and robust healthcare infrastructures that can swiftly respond to outbreaks. For readers, staying informed and practising preventive measures is essential as we navigate the ongoing challenges posed by this deadly virus.