Exploring the Importance of the Danube River
Introduction
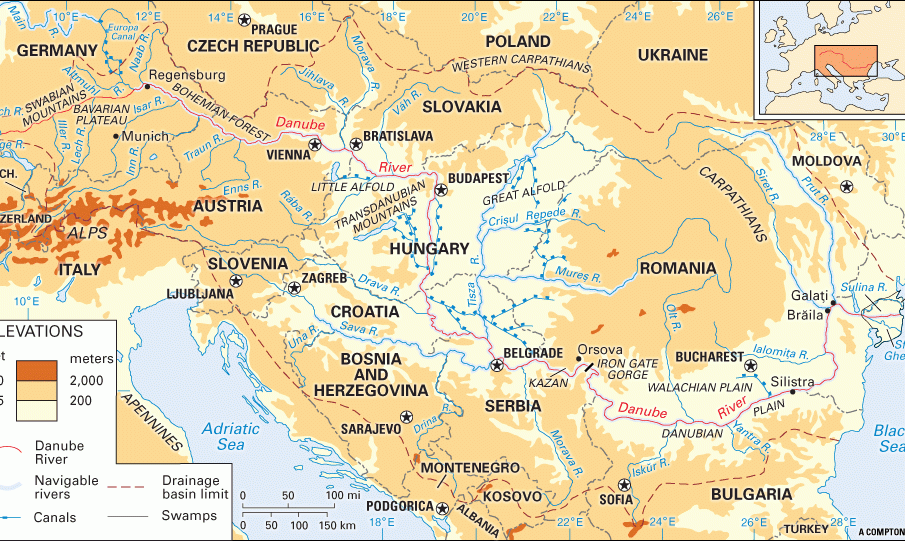
The Danube River, at 2,860 kilometres, is the second-longest river in Europe and holds immense importance for the countries it traverses. Flowing through ten nations, including Germany, Austria, and Romania, this vital waterway serves as a crucial artery for trade, transportation, and cultural exchange. As Europe continues to grapple with climate change and pollution, the Danube’s health and management are increasingly relevant to governmental and environmental organisations.
Current State and Events
In recent years, the Danube has seen a mix of environmental challenges and innovative conservation efforts. The river’s basin hosts over 80 million people and is a lifeline for numerous industries. According to the International Commission for the Protection of the Danube River (ICPDR), climate change has resulted in extreme weather patterns, including severe flooding and droughts that threaten biodiversity and local economies.
In 2023, countries along the Danube have seen collaborative initiatives aiming to address these issues. For instance, Austria and Slovakia launched joint projects focusing on sustainable water management to reduce pollution levels. Moreover, EU funding has been utilised to enhance cross-border cooperation in water quality monitoring and habitat restoration along the riverbanks.
Cultural Significance
The Danube River is not just an ecological resource; it is also steeped in rich cultural history. Each nation it flows through carries unique traditions, culinary practices, and artistic inspirations attributed to the river. Between the vibrant cities of Vienna and Budapest, the river has inspired countless musicians, writers, and filmmakers. UNESCO has also recognised the cultural significance of the Danube, adding certain cultural landscapes along the river to its World Heritage Sites.
Future Prospects
Looking ahead, the future of the Danube River will depend heavily on the actions taken today. It is essential for the nations sharing this vital waterway to continue engaging in cooperation that prioritises environmental sustainability, economic development, and cultural preservation. The recent rise in awareness regarding climate issues among the local populations presents an opportunity for grassroots movements aimed at protecting the river. With concerted efforts, the Danube can maintain its role as a critical resource for generations to come.
Conclusion
The Danube River remains a pillar of ecological and cultural importance in Europe. As countries navigate the challenges posed by climate change, cooperation across borders will be vital. The fate of the Danube encapsulates the broader ecological concerns facing Europe today, making it a key focus for environmental advocates and policymakers alike.