Ethiopia: A Nation of Rich History and Modern Challenges

Introduction
Ethiopia, located in the Horn of Africa, is a nation steeped in rich history and diverse cultures, often renowned as one of the oldest countries in the world. This unique heritage, combined with its strategic location and rapidly growing economy, makes Ethiopia a focal point for international attention. However, the country is currently facing significant challenges, including political turmoil, ethnic tensions, and socioeconomic disparities, which affect its stability and development.
Current Events in Ethiopia
As of late 2023, Ethiopia has been in the news due to a combination of government efforts aimed at economic reform and ongoing conflict in several regions. The Ethiopian government, led by Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed, has been striving to modernise the economy by inviting foreign investment and promoting infrastructure development. However, the nation is still grappling with the aftermath of the Tigray War which began in November 2020, resulting in severe humanitarian crises and displacements.
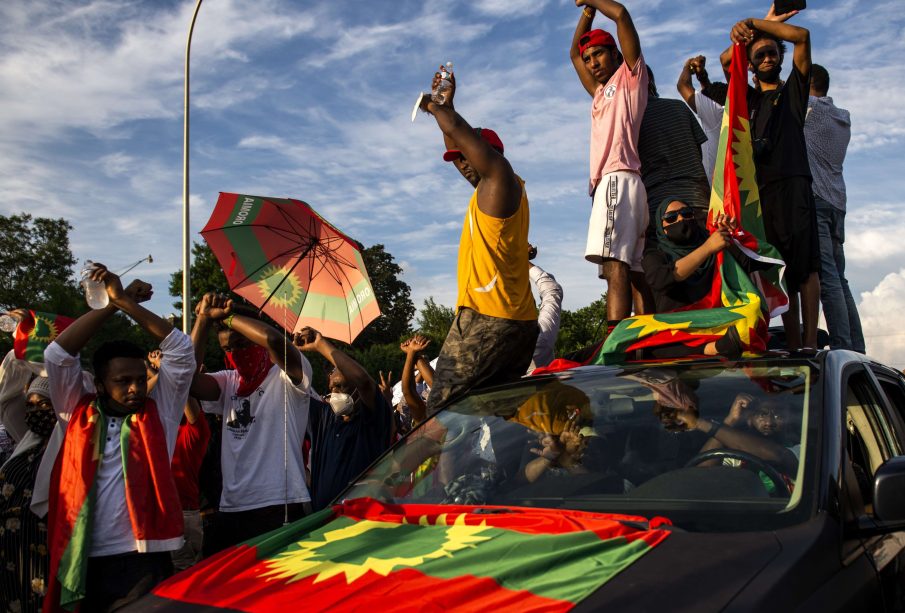
In a recent development, the Ethiopian government has been working with international agencies to address food security and health care needs, services that were greatly disrupted during the conflict. Reports indicate that more than 20 million people in Ethiopia are facing food insecurity as a result of the conflict and climate change impacts. Moreover, the displacement of over two million people highlights the urgency for both governmental and non-governmental organisations to provide essential assistance.
The Cultural Landscape
Ethiopia is not only significant for its political and economic narratives but also for its extraordinary cultural wealth. As the cradle of humanity, it is home to numerous UNESCO World Heritage sites, including the rock-hewn churches of Lalibela and the ancient city of Aksum. The ethnic diversity of Ethiopia, with over 80 distinct groups, contributes to a rich tapestry of languages, traditions, and religious practices, including Christianity and Islam, making it a melting pot of cultures.
Conclusion
The trajectory of Ethiopia remains a focal point for many observers. While economic growth prospects are promising, the country must navigate a landscape marked by social unrest and humanitarian needs. As Ethiopia works towards fostering a peaceful future, how the government engages its citizens and addresses longstanding ethnic grievances will be crucial. Observers anticipate that ongoing reforms, combined with international support, could herald a new chapter for Ethiopia, potentially stabilising the region and showcasing the resilience of its people. For readers interested in global affairs, Ethiopia serves as an important case study of the interplay between history, culture, and contemporary challenges.