Djibouti: A Strategic Hub in the Horn of Africa
Introduction
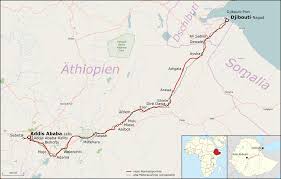
Djibouti, a small country located in the Horn of Africa, has gained increasing importance on the global stage due to its strategic geographical position. Bordered by the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden, Djibouti is positioned near some of the world’s busiest shipping lanes, making it a crucial hub for international trade and military operations. In recent years, the country has became a focal point for foreign investments and has attracted major powers looking to expand their influence in the region.
Geopolitical Significance
Djibouti’s significance is underscored by its hosts to several foreign military bases, including those of the United States, France, and China, contributing to its role in regional security and anti-terrorism efforts. The US military base in Djibouti is known as Camp Lemonnier and serves as a pivotal point for counter-terrorism operations in the region. In 2017, China opened its first overseas military base in Djibouti, reaffirming the country’s growing importance in global geopolitical dynamics.
Economic Developments
The Djiboutian economy heavily relies on its strategic location, with the Port of Djibouti serving as a critical maritime gateway for landlocked countries like Ethiopia. The government’s efforts to modernize and expand port facilities have seen a boost in trade that is vital not only for Djibouti but also for its neighbouring nations. In recent years, Djibouti has also seen significant investments in infrastructure development, including the construction of railways and free trade zones, further solidifying its role as a commercial centre in the region.
Sociopolitical Challenges
Despite its strategic advantages, Djibouti faces several challenges, including issues related to governance, economic inequality, and social unrest. The country has experienced protests against rising living costs and perceived governmental corruption. Nonetheless, the government maintains a tight grip on political power, which raises questions on the long-term sustainability of its current governance structure.
Conclusion
As Djibouti continues to develop its infrastructure and attract foreign investment, its importance in global trade and military strategy is expected to grow. The nation’s strategic location affords it a unique opportunity to become a leading commercial and military hub in the Horn of Africa. However, it will need to navigate its sociopolitical challenges to ensure stability and growth in the coming years. For readers, understanding Djibouti’s role in these global dynamics provides a clearer picture of the shifting sands of geopolitics in the region.








