Cladribine: A Promising Therapy for Multiple Sclerosis
Introduction to Cladribine
Cladribine, a medication originally developed for cancer treatment, is gaining attention for its potential in treating multiple sclerosis (MS), a debilitating autoimmune disease affecting the nervous system. Given the rising prevalence of MS globally, cladribine’s distinct mechanism of action offers a fresh approach in disease management, making it an important topic for discussion among healthcare professionals and patients alike.
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis can cause a variety of symptoms, including fatigue, motor control issues, and cognitive disturbances. It affects more than 2.8 million people worldwide, with recent studies indicating an increase in diagnosis rates over the last decade. Traditional treatments have varied efficacy, leading to a search for more effective therapies.
Cladribine: Mechanism of Action and Administration
Cladribine is a synthetic purine nucleoside that selectively targets lymphocytes, reducing the autoimmune response that damages nerve fibres. The drug is administered in a short-term regimen, with two treatment courses annually, presenting a convenient option for patients compared to the constant daily medication required by other therapies.
Clinical Trials and Efficacy
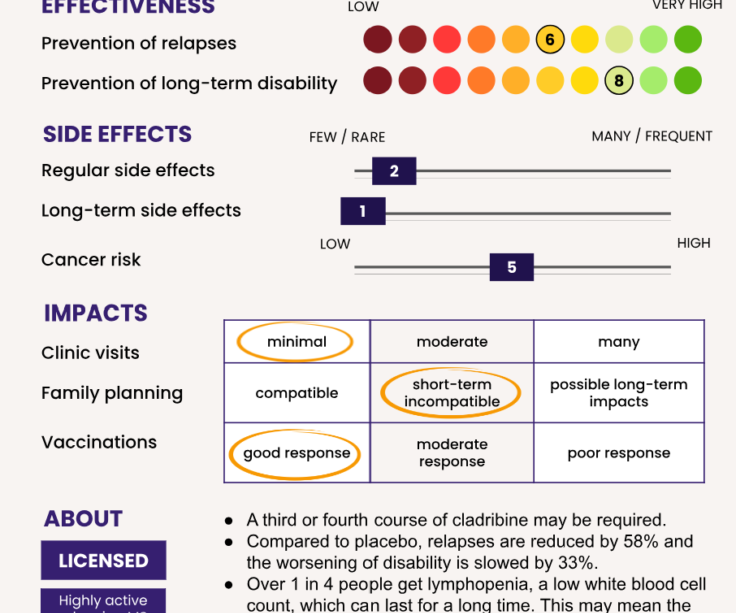
Recent clinical trials, including the CLARITY study, have shown that cladribine significantly reduces the frequency of MS relapses and slows disease progression. It has been shown to decrease the number of new brain lesions as observed through MRI scans. As a result, cladribine has received approval in numerous countries under various trade names, such as Mavenclad in the UK.
Adverse Effects and Considerations
Despite its promise, cladribine is not without risks. Patients must be monitored for infections due to lymphocyte depletion, and it may not be suitable for individuals with certain health conditions. Potential side effects include headache, nausea, and fatigue. Healthcare professionals must weigh the benefits against the risks when prescribing this therapy.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
As research continues, cladribine remains a beacon of hope for individuals living with multiple sclerosis. Its unique approach and clinical efficacy could redefine treatment protocols in the coming years. As data emerges, cladribine may further establish itself as a mainstay in managing this chronic condition, providing patients with a better quality of life and reducing the overall burden of MS. With an increasing need for effective treatments, cladribine’s role in clinical practice is set to expand, highlighting the importance of ongoing research and patient education.