An Insight into US Government Shutdowns: Causes and Consequences
Introduction
US government shutdowns have emerged as a significant phenomenon in American politics, impacting millions of citizens and the economy. These shutdowns occur when Congress fails to pass sufficient funding for government operations, leading to the temporary cessation of federal activities. Understanding the implications of these shutdowns is crucial, especially as recent events have highlighted the frequency and complexity of this issue.
Recent Shutdown Events
The most recent government shutdown occurred from December 2022 to January 2023, lasting 35 days and affecting approximately 800,000 federal employees. The shutdown was a result of a stalemate between the House and Senate over budget allocations and critical funding for various federal programmes. During this period, many government services were halted, and employees were either furloughed or forced to work without pay, highlighting the profound personal and economic repercussions of such political gridlocks.
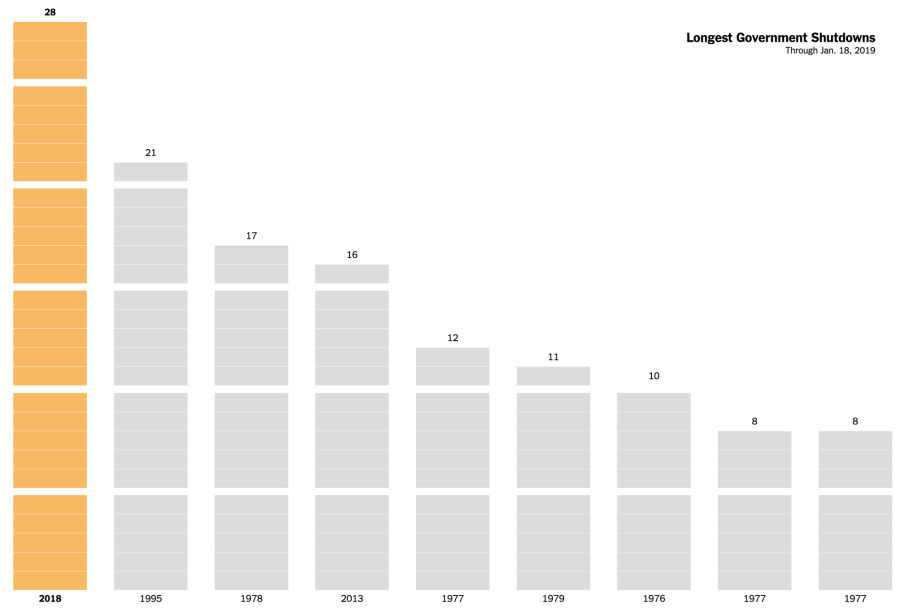
Historically, the United States has experienced numerous government shutdowns since the first in 1980. The reasons often vary, but they predominantly stem from budget disagreements, partisan politics, and the prioritisation of different spending bills. The immediate fallout includes delayed payroll for federal workers, disruptions in services including national parks and research institutions, and overall economic uncertainty.
The Economic and Social Impact
The economic impact of government shutdowns can be substantial. According to a report by the Congressional Budget Office, the 35-day shutdown in early 2019 cost the economy approximately $11 billion, with a projected loss of $3 billion that would not be recovered. Local businesses, federal contractors, and surrounding communities suffer from diminished consumer spending and lost revenue during shutdowns.
Moreover, the social effects extend beyond the economy. Families relying on federal paychecks for their financial stability face hardships, including missed mortgage payments and increased stress levels. The uncertainty surrounding the reopening of government services can also disrupt essential services such as the administration of social security and food assistance programmes.
Conclusion
The cycle of US government shutdowns raises questions about the effectiveness of political negotiations and the potential need for reforms in the budgeting process. As Congress continues to grapple with budgetary priorities, the ramifications of shutdowns remain a critical issue for policymakers and citizens alike. Forecasts suggest that without systemic changes, future shutdowns may remain a recurring problem, further emphasizing the importance of finding bipartisan solutions to fiscal disagreements. Understanding the broader implications of these shutdowns is essential for constituents, as they navigate the complex landscape of American governance.









