All About the Great White Shark: Nature’s Apex Predator

Introduction
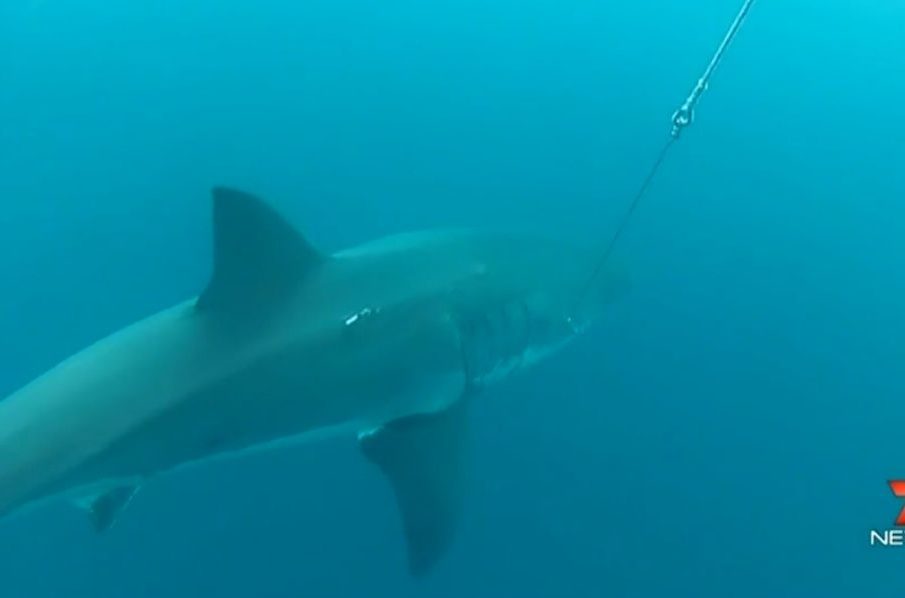
The great white shark (Carcharodon carcharias) holds a significant place in marine ecosystems and popular culture. It is renowned not only for its formidable hunting prowess but also for its complex biology and behaviour. Understanding this apex predator is crucial for marine conservation efforts and promoting awareness about ocean health.
Habitat and Distribution
Great white sharks are found in temperate coastal waters across the globe, including the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans. They are known to inhabit regions rich in marine life, such as seal colonies, which form a key part of their diet. Notable locations for sightings include the coasts of California, South Africa, and Australia. Current research indicates that these sharks may also engage in long-distance migration, travelling thousands of miles between feeding and breeding grounds.
Behaviour and Diet
As carnivorous predators, great white sharks primarily feed on marine mammals such as seals, but they also consume fish and carrion. Their hunting technique includes breaching the water surface to surprise their prey. This behaviour, combined with their keen sense of smell, makes them efficient hunters. Recent studies have revealed that they may exhibit complex social behaviours, challenging the stereotype of the solitary predator.
Conservation Status
Despite their fearsome reputation, great white sharks are classified as vulnerable by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). They face various threats, including overfishing, bycatch, and habitat loss due to human activities. The rise of shark finning and illegal fishing practices has further exacerbated their decline. Global conservation efforts are crucial, focusing on protective legislation and raising public awareness about the importance of ecological balance.
Conclusion
The great white shark continues to captivate and intrigue both the scientific community and the public. As top predators, their presence is vital for maintaining marine ecosystem health. By fostering a better understanding and appreciation of great white sharks, we can bolster conservation efforts and ensure their survival for future generations. Continued research and public education will play essential roles in achieving these goals, encouraging a sustainable coexistence between humans and these magnificent creatures.