A Comprehensive Guide to Inheritance Tax in the UK
Introduction
Inheritance tax is a significant financial consideration for many families in the UK, affecting the transfer of wealth from one generation to the next. As property values rise, understanding the nuances of inheritance tax has never been more critical. It can influence how estates are planned, whether through wills or trusts, and the tax implications can significantly affect heirs’ inheritances.
Current Inheritance Tax Framework
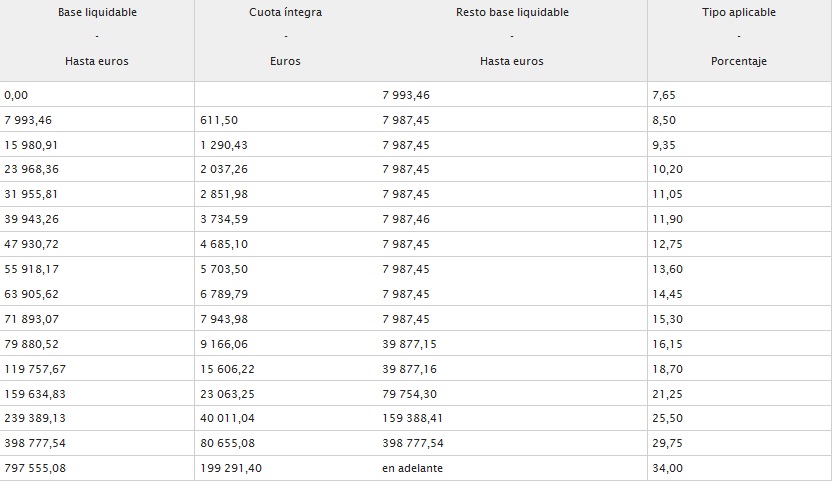
As of October 2023, inheritance tax applies to estates valued over £325,000, with a standard rate of 40% on the amount exceeding this threshold. However, there are several reliefs and exemptions available that can reduce or negate the tax due. For instance, if the estate is passed on to children or grandchildren, the nil-rate band increases to £500,000.
Additionally, gifts made during a person’s lifetime can also affect inheritance tax calculations. Gifts are typically exempt if made more than seven years before death, but there are annual exemptions, including £3,000 per donor, which can be carried forward to the next year if not fully used.
Recent Developments and Considerations
The current economic landscape has prompted discussions regarding potential changes to the inheritance tax system. As the UK faces financial pressures from recovering from the pandemic and rising cost of living, calls for reform are intensifying. Some suggest lowering the threshold for taxation, while others advocate for maintaining the status quo in light of the benefits to revenue generation.
In 2023, the government conducted a review of inheritance tax which is expected to yield recommendations in the upcoming budget. Advocates for reform argue that the current system fails to account for regional disparities in property values, disproportionately affecting those in high-value areas.
The Importance of Estate Planning
Given the complexity surrounding inheritance tax, effective estate planning is essential. Consulting with financial advisors or estate planners can help ensure that tax liabilities are minimised and that beneficiaries receive as much of the estate as possible. Establishing trusts or making full use of gift exemptions can be viable strategies in reducing overall tax burdens.
Conclusion
Inheritance tax remains a crucial yet complicated aspect of estate planning in the UK. With ongoing discussions about possible reforms and the current thresholds, property owners and families must stay informed about their options. Engaging with professional advisors can ensure that estates are managed effectively, ultimately securing financial legacies for future generations.







