Insights into Lewy Body Dementia: Symptoms and Research Updates
Introduction
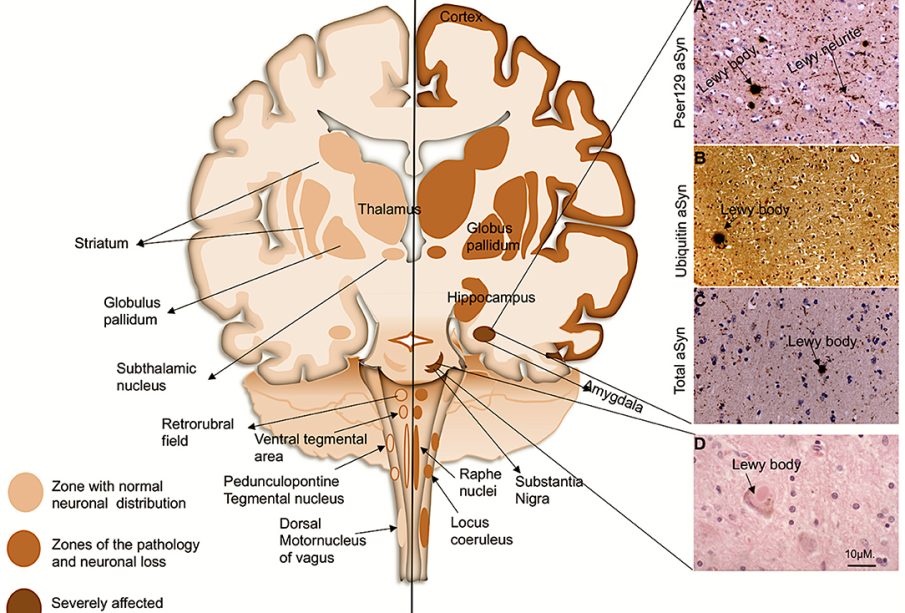
Lewy Body Dementia (LBD) is a complex and serious neurological condition that is the second most common type of progressive dementia after Alzheimer’s disease. Characterised by the abnormal aggregation of proteins known as Lewy bodies in the brain, LBD affects both cognitive and physical functioning, leading to a variety of symptoms such as fluctuating cognition, visual hallucinations, and motor issues similar to Parkinson’s disease. As awareness of this condition grows, understanding its implications is vital, not only for patients and their families but also for healthcare providers and researchers working to advance treatment strategies.
Details on Lewy Body Dementia
Symptoms of LBD typically present in three categories: cognitive, visual, and motor. Cognitively, individuals may experience fluctuations in attention and alertness, memory difficulties, and challenges in problem solving. Visually, up to 80% of patients may suffer from vivid hallucinations, which can be distressing. The motor symptoms may resemble those of Parkinson’s disease, including stiffness, balance issues, and tremors.
Diagnosing LBD can be challenging as its symptoms often overlap with other types of dementia and conditions like Parkinson’s Disease. Typically, specialists conduct a thorough assessment including medical history, cognitive tests, and sometimes neurological examinations. Imaging techniques such as MRI or PET scans may help in ruling out other conditions.
Recent Research and Developments
Recent studies have highlighted advances in understanding Lewy Body Dementia. For instance, a study published in the Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease in 2023 discussed the effectiveness of certain cholinesterase inhibitors commonly used in Alzheimer’s treatment, indicating they may also benefit LBD patients by alleviating cognitive symptoms.
Furthermore, researchers are examining the role of neuroinflammation in LBD, suggesting that addressing inflammation could play a crucial role in slowing disease progression. Clinical trials are ongoing, and collaborations between universities and pharmaceutical companies are ramping up to develop effective therapies tailored to LBD patients.
Conclusion
Lewy Body Dementia remains a challenging condition for both patients and caregivers, but the increased recognition and understanding of this disease are crucial. Ongoing research holds promise for better treatment options and support strategies. As findings progress, stakeholders in healthcare must prioritize education and resources for families affected by LBD, ensuring they receive the support they need and enhancing quality of life for those living with this condition.









