Understanding the Bubonic Plague: Past and Present
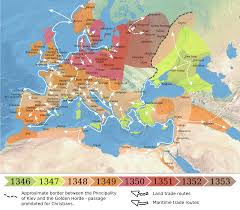
Introduction: The Bubonic Plague’s Enduring Impact
The bubonic plague, notorious for its devastating impact during the Middle Ages, continues to be a relevant topic in public health discussions today. While its most infamous outbreak occurred in the 14th century, the disease caused by the bacterium *Yersinia pestis* has not vanished entirely. Recent cases in various regions remind us of the importance of awareness and medical preparedness regarding this ancient foe.
Current Events and Resurgence
As of 2023, health authorities report sporadic cases of bubonic plague in certain parts of the world, particularly in rural areas of the western United States and parts of Africa and Asia. In June 2021, for example, a handful of plague cases were reported in the Democratic Republic of Congo, prompting health officials to ramp up public health measures. Despite its notoriety, the bubonic plague is treatable with antibiotics if caught early, yet concerns persist due to occasional reports of antibiotic-resistant strains.
Moreover, recent research has shed light on the role of climate change in the evolution of bacterial pathogens. Increasing temperatures and changing ecosystems may alter the habitats of fleas and rodent populations that carry *Yersinia pestis*, potentially leading to new outbreaks.
The Importance of Vigilance
Public health experts emphasise the need for ongoing surveillance, particularly in areas historically affected by the plague. Awareness campaigns and educational programs are essential to prevent misunderstandings about the disease and to alleviate fears associated with it. For instance, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provides valuable resources about the symptoms, transmission, and prevention of bubonic plague. Engaging in dialogue about historical pandemics, like the bubonic plague, can also offer insights into modern health crises.
Conclusion: What Lies Ahead
The bubonic plague serves as a reminder of the vulnerabilities in human health and the importance of vigilance in public health strategies. While the risk of widespread outbreaks is low owing to modern medical advancements, the disease still poses a threat in certain regions. It is crucial for researchers and public health officials to remain proactive in monitoring its incidence and developing strategies to prevent future cases. By continually educating the public and maintaining awareness, societies can better prepare for and respond to this threat, ensuring that the lessons of history are not forgotten.









