Understanding the Bank of England Base Rate and Its Implications
Introduction
The Bank of England base rate is a critical economic indicator that influences lending rates, inflation, and overall economic stability. Recently, the base rate has gained heightened attention as the UK grapples with rising inflation and economic recovery challenges. Monitoring changes in this rate is essential for both consumers and businesses, as it can significantly affect borrowing costs and savings interest rates.
Recent Developments
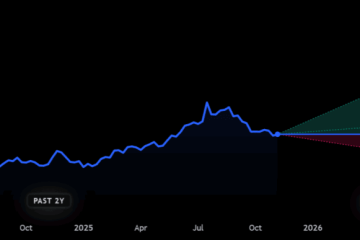
As of October 2023, the Bank of England has raised the base rate to 5.25%, up from 4.75% earlier in the year. This decision was largely driven by the need to combat soaring inflation, which has been consistently above the central bank’s target of 2%. The recent hike marks the thirteenth consecutive increase since late 2021, a sign of the bank’s commitment to stabilising the economy amidst ongoing cost-of-living pressures.
In the latest Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) meeting, several key considerations influenced the decision to raise the rate. Among those was the latest inflation data, demonstrating an annual inflation rate of 6.7%. The MPC concluded that further increases may be necessary to prevent inflation from becoming entrenched. Additionally, employment rates in certain sectors have also affected the economic landscape, with the labour market remaining tight.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The hike in the base rate impacts various sectors of the economy. For consumers, borrowing costs are rising, especially for mortgages and personal loans. Homeowners on variable interest rates are expected to see a direct increase in their monthly payments, which may affect disposable income and consumer spending.
Businesses, too, are likely to feel the pinch as the cost of borrowing escalates. Small businesses that rely on loans for expansion or operational needs could reconsider their investment strategies. Conversely, higher interest rates may benefit savers, as banks and financial institutions start to offer better returns on savings accounts.
Conclusion
The Bank of England’s base rate continues to be a pivotal variable in the UK economic landscape. With inflation persisting above target, the ongoing adjustments to the base rate indicate a proactive response to economic challenges. Economists predict that if inflation does not show signs of slowing soon, we may witness further increases in the base rate into 2024. It remains crucial for consumers and businesses to closely monitor these changes, as they can significantly impact financial planning and economic growth in the months ahead.