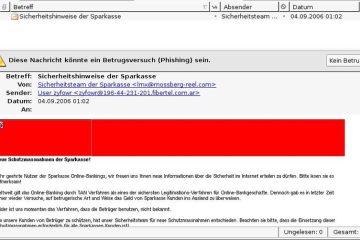
The Significance of ID Verification in the Digital Age

Introduction
In an increasingly digital world, the concept of identification (ID) has become paramount. With the surge in online transactions, remote working, and digital services, the need for secure and reliable identity verification methods has never been more crucial. The significance of ID extends beyond mere authentication; it impacts security, privacy, and access to essential services.
Current Trends in ID Verification
Recent events, including the rise of cybercrime and data breaches, have accelerated the evolution of ID verification technologies. According to recent reports from the Cyber Security Authority, identity theft remains one of the most prevalent forms of cybercrime, prompting businesses and government agencies to enhance their verification processes.
In response to these challenges, various sectors are adopting advanced technologies such as biometrics, artificial intelligence (AI), and blockchain. For instance, biometric systems, which include fingerprint scanning and facial recognition, offer a higher level of security compared to traditional password systems. AI-powered verification systems are also making strides by analysing user behaviour patterns to detect anomalies that may indicate fraud.
Legislative Developments
On the legislative front, regulations surrounding ID verification are evolving. The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has set a benchmark for data protection and privacy, demanding stringent measures for personal data handling, including ID verification methods. Similarly, the UK’s approach to data rights is being shaped by both GDPR and local regulations, leading to a holistic examination of how companies manage consumer identities.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite technological advancements, challenges persist. Privacy concerns are at the forefront, with individuals wary of how their personal information is stored and utilised. Moreover, disparities in access to technology raise questions regarding equity, especially for vulnerable populations who may face difficulties in obtaining valid IDs.
Conclusion
The implications of effective ID verification are profound, influencing not only individual security but also broader economic stability. As organisations and governments continue to innovate and adapt security measures, the focus must remain on striking a balance between accessibility, privacy, and security. By prioritising robust ID verification methods, society can foster a safer, more secure environment in the digital landscape. Looking ahead, further advancements and regulatory frameworks will likely shape how identities are verified, ensuring a secure future for all digital interactions.