Understanding Gonorrhea: Current Trends and Implications
Introduction to Gonorrhea
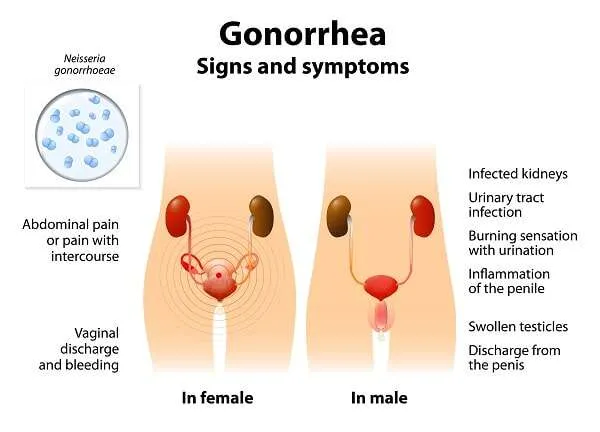
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It primarily affects the mucous membranes of the urogenital tract, but it can also infect the throat and rectum. The importance of addressing gonorrhea lies not only in its impact on individual health but also in its potential to contribute to wider public health concerns, such as antibiotic resistance and increased vulnerability to HIV.
Current Statistics and Trends
Recent data from Public Health England indicates a worrying trend in the rise of gonorrhea cases. In 2022, there were over 100,000 reported cases, marking an 18% increase compared to the previous year. This surge is particularly pronounced among young adults aged 15 to 24 years, which is consistent with findings from other countries experiencing similar outbreaks.
Factors contributing to this increase include a decline in condom use, enhanced screening and testing in sexual health clinics, and the stigma surrounding STIs that may discourage individuals from seeking treatment. Moreover, the relaxation of certain lockdown measures post-COVID-19 has led to an increase in sexual activity, further amplifying the risk of transmission.
Public Health Response and Prevention
In response to the rising rates of gonorrhea, health authorities have ramped up efforts to educate the public about safe sex practices. Initiatives include promoting the use of condoms, encouraging regular STI testing, and increasing accessibility to treatment for those infected. Furthermore, public health campaigns aim to reduce the stigma associated with STIs, helping to ensure that people feel comfortable seeking help.
Antibiotic resistance is another significant concern regarding gonorrhea management. The World Health Organization (WHO) has classified gonorrhea as a high priority organism due to its growing resistance to common antibiotic treatments. This has led to calls for enhanced surveillance of antibiotic efficacy and the development of new treatment protocols.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
Addressing the rise in gonorrhea cases is crucial for public health. Continued education on safe sexual practices, coupled with increased testing and enhanced treatment protocols, can help stem the tide of this STI. The rising prevalence of antibiotic resistance presents a significant challenge, underscoring the need for ongoing research and innovation in both treatment strategies and public health messaging. As communities work together to combat this issue, prioritising safe sex, regular testing, and open conversations about STIs remain vital in curbing the rates of gonorrhea and improving overall sexual health.