Understanding the Current UK Inflation Rate and Its Implications
Introduction
The inflation rate in the United Kingdom is a critical economic indicator that affects policies, consumer behaviour, and overall economic health. As of late 2023, inflation concerns have come to the forefront, influencing decisions by the Bank of England and impacting daily life for millions of Britons. Understanding the current UK inflation rate is essential for grasping the broader economic landscape, which is characterised by rising prices and shifting financial strategies.
Current Inflation Trends
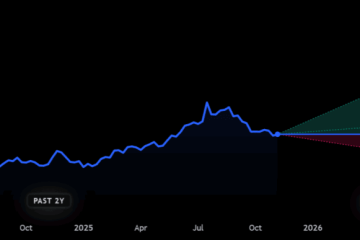
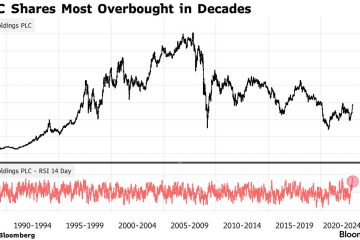
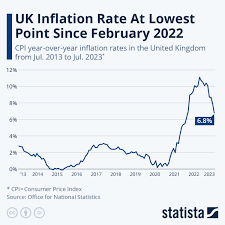
As reported by the Office for National Statistics (ONS), the annual inflation rate in the UK rose to 6.7% in October 2023, representing a slight increase from 6.4% in September. This uptick is primarily attributed to soaring energy and food prices, both of which have been sporadically volatile since the onset of the pandemic and the energy crisis stemming from geopolitical tensions.
The Bank of England has set an inflation target of 2%, and the persistent inflationary pressures have led to ongoing discussions regarding interest rate adjustments. Following a series of rate hikes throughout 2022 and early 2023, the central bank’s monetary policy committee has been weighing the impacts of further increases against the potential for economic slowdown.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The rising inflation rate has significant implications for consumers, leading to increased costs for essentials such as groceries and fuel. Households are feeling the pinch as disposable incomes struggle to keep pace with these rising prices. Recent surveys indicate that over half of UK families have altered their spending habits, opting for cheaper alternatives or cutting back on non-essential items.
Moreover, businesses are also experiencing the effects of inflation, facing higher operational costs, which can lead to increased prices for consumers. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are particularly vulnerable, with many struggling to maintain profit margins amid rising costs. As a result, some businesses are considering staff reductions or delaying expansion plans to weather the storm.
Future Projections
Looking ahead, economists are divided on the trajectory of the inflation rate. While some predict a gradual decline in inflation rates as global supply chains stabilise and energy prices moderate, others anticipate that stubborn factors such as wage increases will keep inflation elevated. The Bank of England is set to meet next month to discuss its monetary policy stance, with analysts closely watching for indications on interest rate changes as inflationary pressures evolve.
Conclusion
In summary, the current UK inflation rate is not merely a number; it reflects complex interactions within the economy affecting both individuals and businesses. As stakeholders navigate these turbulent waters, observing how the Bank of England responds and how the economic landscape evolves will be crucial for understanding the inflation outlook. For consumers, adapting spending habits and planning budgets in the face of ongoing inflation remains essential.