Understanding Parkinson’s Disease: Symptoms and Current Insights
Introduction
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement, causing tremors, stiffness, and balance issues. According to the Parkinson’s Foundation, approximately 145,000 people in the UK are living with the condition, and this number is expected to rise as the population ages. With advancements in research and treatment options, understanding Parkinson’s has become increasingly important in order to enhance patients’ quality of life and develop effective interventions.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
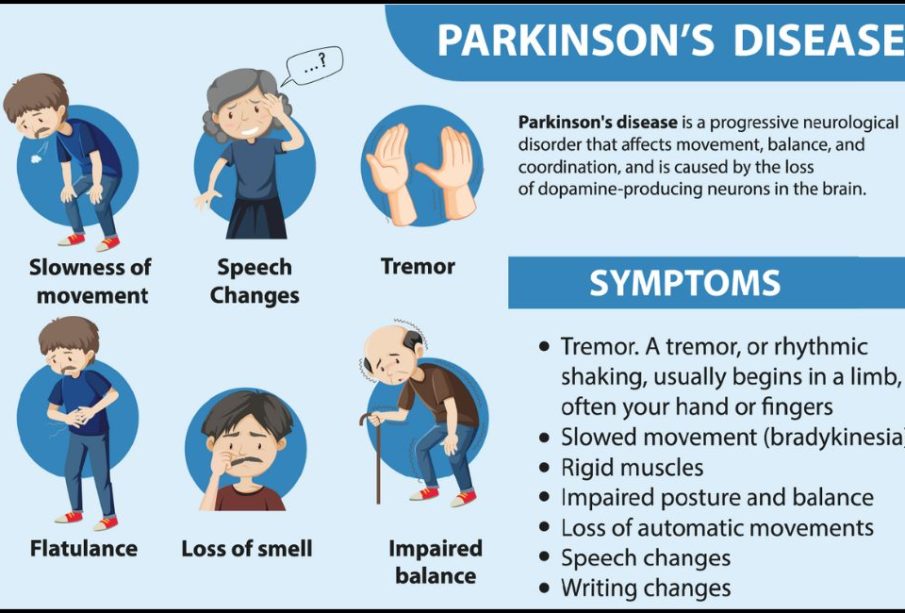
The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease typically develop gradually and may vary significantly among individuals. Common symptoms include involuntary shaking, difficulty with balance and coordination, and rigidity of the limbs. Non-motor symptoms such as sleep disturbances, depression, and cognitive changes can also significantly affect daily life.
Diagnosis often involves a comprehensive evaluation by a neurologist who assesses medical history, symptoms, and physical examination findings, as there are currently no definitive tests for the illness.
Latest Research Developments
Recent research initiatives have focused on better understanding the causes of Parkinson’s disease and exploring novel therapeutic strategies. A promising study published in the journal “Nature” in September 2023 identified a potential biomarker for the early detection of Parkinson’s. Researchers found abnormalities in a specific protein known as alpha-synuclein, which is believed to play a crucial role in the disease’s pathology. Detecting these changes early could lead to earlier interventions and better outcomes for patients.
Moreover, advancements in gene therapy are gaining traction, with several clinical trials underway to evaluate the safety and efficacy of new treatments targeting the underlying genetic components of Parkinson’s. One such trial, expected to conclude in late 2024, aims to provide insights into whether gene editing can effectively slow disease progression.
Conclusion
Parkinson’s disease presents significant challenges not only for patients but also for caregivers and health systems. As our understanding continues to evolve with ongoing research, advances in early diagnosis and treatment could significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by the disease. Furthermore, public awareness and education about Parkinson’s remain critical for fostering a supportive environment for those living with the condition. The future holds potential for improved interventions that may change the course of this complex disease.