Understanding RPI and Its Economic Impact
Introduction to RPI
The Retail Prices Index (RPI) is a crucial measure of inflation in the United Kingdom, reflecting the change in the cost of a basket of retail goods and services. Understanding RPI’s trends and implications is essential for consumers, businesses, and policymakers as it affects economic decisions, wages, and inflation adjustments. Recent discussions around RPI have highlighted its relevance in today’s economic landscape, especially in the context of rising living costs and economic recovery.
Current RPI Trends
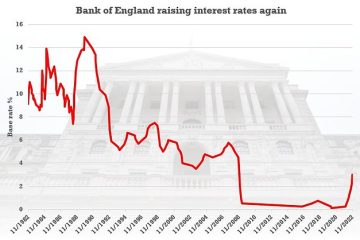
Recent data from the Office for National Statistics (ONS) reveals that the RPI rose by 5.1% in August 2023 compared to the previous year, demonstrating persisting inflationary pressures in the UK. This rise can be attributed to increasing prices in various sectors, including housing, transportation, and food. Analysts suggest that the ongoing repercussions of the pandemic, coupled with geopolitical tensions and supply chain challenges, have contributed to these sustained inflation rates. The RPI’s movements are closely monitored as they can directly influence interest rates set by the Bank of England.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
For consumers, the rising RPI means that purchasing power is diminished, with everyday expenses continuing to escalate. Households are feeling the pinch, as essential goods and services become pricier. Moreover, businesses must navigate these changes to retain competitiveness, which may lead to higher prices passed onto consumers. The retail sector, heavily influenced by RPI, is facing challenges as consumer spending habits shift in response to rising costs, which could impact economic recovery efforts.
Forecasting the Future of RPI
Looking ahead, the RPI is expected to remain a key indicator of economic health throughout 2024. Experts suggest that while inflation may gradually decrease due to stabilising factors in the economy, persistent rises in energy and food prices could sustain higher RPI rates. Policymakers may need to consider alternative measures such as the Consumer Prices Index (CPI), which excludes certain volatile costs, to better capture inflation trends moving forward. Understanding shifts in RPI will be crucial for individuals and businesses alike as they prepare for the economic landscape in 2024 and beyond.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Retail Prices Index serves as an important benchmark for economic analysis in the UK. As we continue to navigate a post-pandemic economy, understanding RPI’s trends will be essential for gauging both consumer behaviour and the overall economic climate. Stakeholders must remain vigilant and adapt to these changes, ensuring that they are prepared for the implications of rising inflationary pressures on finances and business operations.