Bilateral Pneumonia: Risk Factors and Treatment Approaches
Introduction
Bilateral pneumonia is a serious respiratory condition where inflammation affects both lungs simultaneously, often resulting from infections such as bacteria, viruses, or fungi. This condition is crucial to understand, especially in light of recent global health crises that have highlighted the vulnerabilities of respiratory systems. With rates of pneumonia, particularly bilateral forms, increasing globally, medical professionals emphasize the need for awareness and education regarding symptoms, causes, and effective treatment methods.
Current Statistics and Causes
According to Public Health England, pneumonia remains one of the top causes of hospitalisation in the UK, with a significant number of cases attributed to bilateral infections. Common pathogens identified include Streptococcus pneumoniae and various strains of influenza virus. Other risk factors contributing to bilateral pneumonia include weakened immune systems, chronic health conditions (like asthma and COPD), smoking, and exposure to environmental pollutants.
Recent Outbreaks
In recent months, health departments across the UK have reported an uptick in pneumonia cases associated with the flu season starting earlier than usual. Hospitals are seeing more individuals presenting with bilateral pneumonia, often following seasonal influenza infections. The NHS has indicated that vaccination efforts are vital in mitigating these outbreaks. They advise individuals, particularly older adults and those with underlying health conditions, to receive seasonal flu and pneumonia vaccinations to reduce their risk.
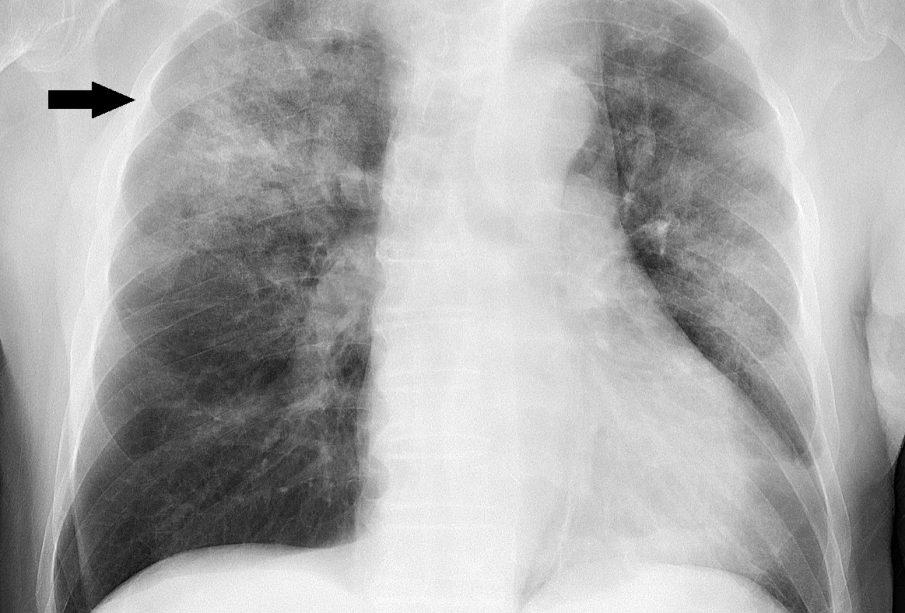
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Symptoms of bilateral pneumonia can include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain. In severe cases, patients may experience confusion or altered mental states due to low oxygen levels. Diagnosis typically involves clinical assessments, chest X-rays, and sometimes CT scans to determine the extent of lung involvement. Early diagnosis is critical as it significantly impacts treatment outcomes.
Treatment Options
Treatment for bilateral pneumonia often consists of antibiotics for bacterial infections, antiviral medications for viral cases, and supportive care, including oxygen therapy and fluid management. Early intervention is vital; hospitalisation may be necessary for severe cases, particularly for those at increased risk of complications.
Conclusion
Bilateral pneumonia represents a significant health threat, particularly in vulnerable populations. Public health initiatives emphasizing vaccination and early detection are crucial in combatting its prevalence. As patterns of respiratory infections evolve, ongoing research and community awareness remain essential in mitigating the impact of bilateral pneumonia on public health. By understanding the risks and recognising symptoms early, patients can seek medical advice promptly, potentially leading to better health outcomes.