Understanding UK Inflation: Current Trends and Impacts
The Significance of UK Inflation
UK inflation has become a critical economic indicator, reflecting the purchasing power of consumers and the overall health of the economy. As the Bank of England monitors price changes, fluctuations in inflation rates significantly influence monetary policy, consumer behaviour, and economic growth. As the UK faces various challenges, understanding inflation is essential for individuals and businesses alike.
Current Inflation Rates
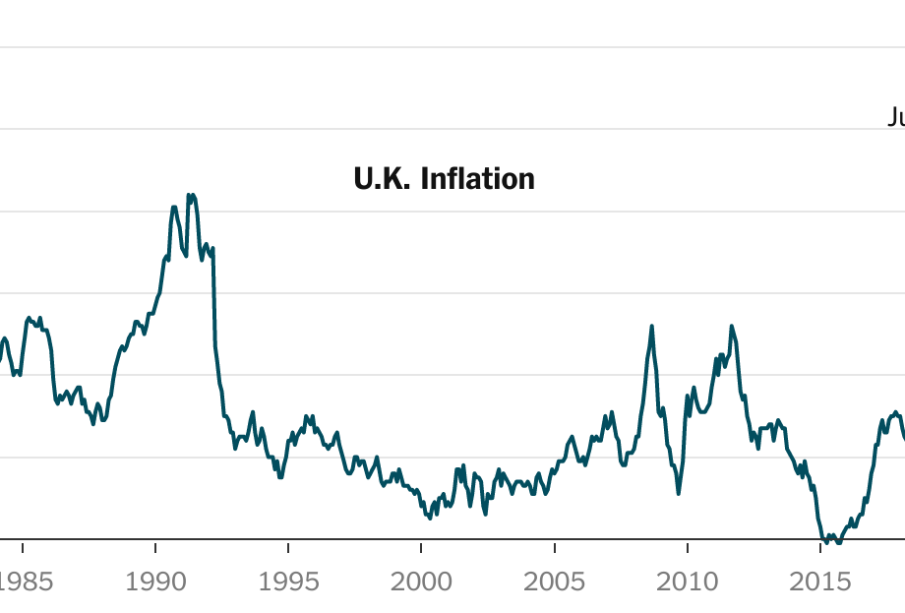
As of October 2023, UK inflation has witnessed significant volatility, primarily driven by external factors such as global supply chain disruptions and rising energy prices. According to the Office for National Statistics (ONS), the Consumer Prices Index (CPI) recorded an annual inflation rate of 6.7% in September 2023, a slight decrease from the peak levels observed earlier this year. Comparatively, inflation had surged above 9% within the last year, leading to financial strain on households and increased cost of living, making the present rate a point of relief yet still concerning.
Causes of Inflation
The ongoing inflation can be attributed to a combination of factors. The economic repercussions from the COVID-19 pandemic, coupled with the conflict in Ukraine, have disrupted supply chains and inflated energy costs. Additionally, demand rebounds in sectors like travel and hospitality have accelerated pricing pressures, reflecting consumer recovery behaviour post-pandemic. Rising costs of raw materials and labour further contribute to persistent inflationary pressures, complicating the efforts for economic recovery.
Effect on Households and Businesses
The implications of rising inflation extend to every corner of the UK economy. Households are increasingly tightening their budgets, as essential goods become more expensive, leading to shifts in spending patterns. Notably, food and utility costs have posed significant challenges for low- and middle-income families. For businesses, particularly small enterprises, higher operational expenses can lead to tough decisions involving pricing strategies and workforce adjustments as they strive to maintain profitability amidst rising costs.
Future Forecasts and Economic Policies
Looking ahead, economists are cautiously optimistic about the trajectory of UK inflation. While short-term pressures remain, the Bank of England may adjust interest rates to curb inflation and ensure economic stability. The anticipated moderation in inflation rates could herald a more balanced economic environment, allowing for renewed growth in consumer spending and business investment. Observers point out that sustained attention to inflation and prompt policy responses will be vital for fostering economic resilience in the coming months.
Conclusion
In summary, UK inflation continues to be a pivotal issue that will shape both consumer experience and the broader economic landscape. Understanding the factors at play, as well as the broader implications for households and businesses, is essential in navigating the complexities of this economic environment. As we move towards 2024, the significance of monitoring inflation trends will only grow, presenting both challenges and opportunities for all stakeholders involved.